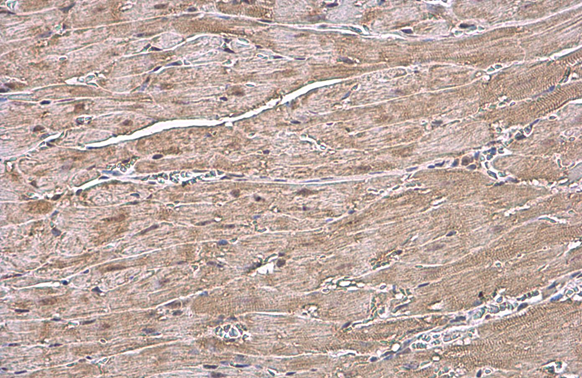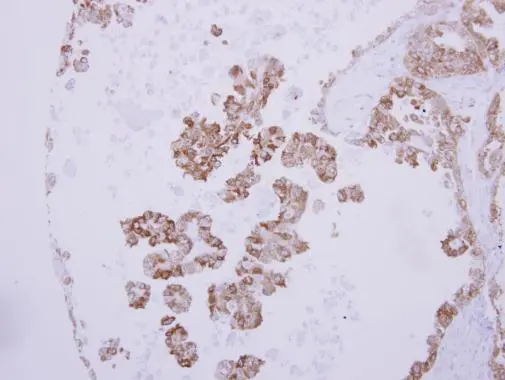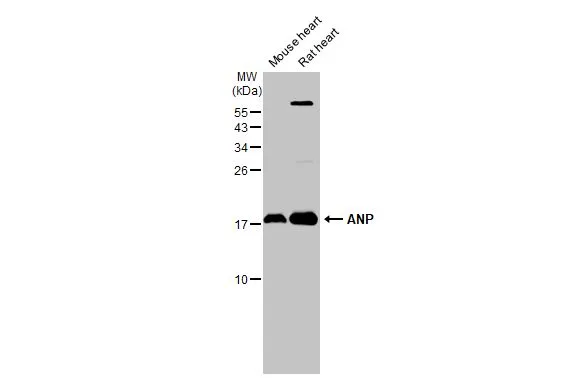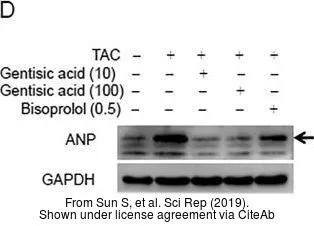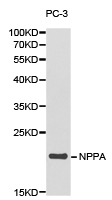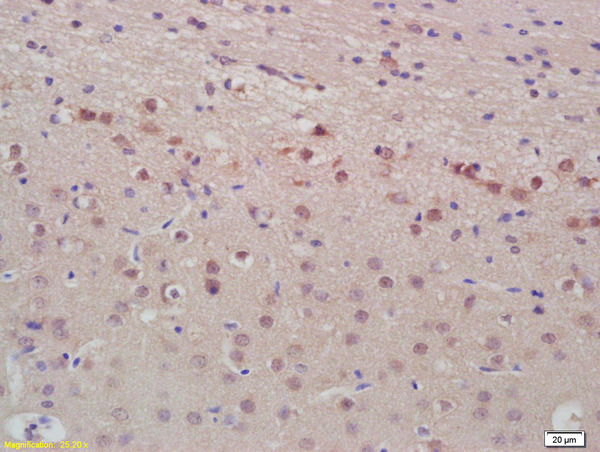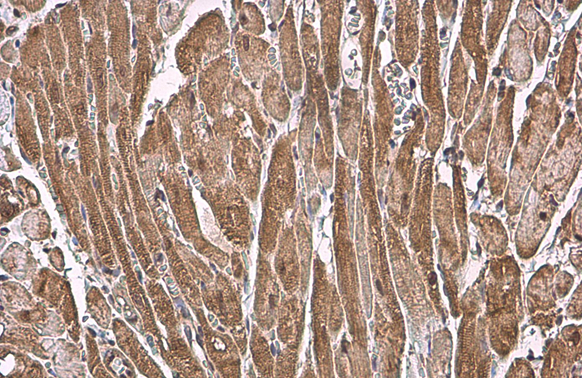
ANP antibody detects ANP protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat heart. ANP stained by ANP antibody (GTX109255) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
ANP antibody
GTX109255
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityAmphibian, Human, Mammals, Mouse, Rat
TargetNPPA
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameANP antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.46 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4878
- Target nameNPPA
- Target descriptionnatriuretic peptide A
- Target synonymsANF, ANP, ATFB6, ATRST2, CDD, CDD-ANF, CDP, PND, natriuretic peptides A, atrial natriuretic factor prohormone, atrial natriuretic peptide prohormone, atriopeptigen, atriopeptin, cardiodilatin-related peptide, cardionatrin, natriuretic peptide precursor A, preproANP, preproCDD-ANF, prepronatriodilatin, proANF, proANP
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01160
- Protein NameNatriuretic peptides A
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to the natriuretic peptide family. Natriuretic peptides are implicated in the control of extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis. This protein is synthesized as a large precursor (containing a signal peptide), which is processed to release a peptide from the N-terminus with similarity to vasoactive peptide, cardiodilatin, and another peptide from the C-terminus with natriuretic-diuretic activity. Mutations in this gene have been associated with atrial fibrillation familial type 6. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityAmphibian, Human, Mammals, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161