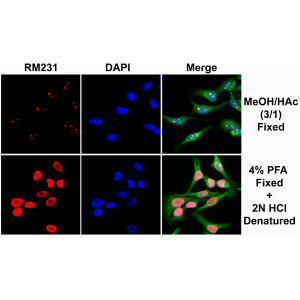
Immunocytochemical staining of HeLa cells using rabbit monoclonal anti-5-mC (clone RM231) antibody (red). Actin filaments have been labeled with fluorescein phalloidin (green), and nuclei stained with DAPI (blue).
anti-5-Methylcytosine (5-mC), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM231)
REV-31-1110-00
ApplicationsDot Blot, Flow Cytometry, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityVertebrate
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-5-Methylcytosine (5-mC), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM231)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsDot Blot, Flow Cytometry, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM231
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific Description5-Methylcytosine is a methylated form of the DNA base cytosine that regulates gene transcription and is involved in epigenetics. It is one of the best known epigentic modifications. This methylation typically occurs at cytosine in CpG dinucleotides in vertebrates. When cytosine is methylated, the DNA maintains the same sequence, but the expression of methylated genes can be altered. 5-Methylcytosine is a very important repressor of transcription in the genome. When present in promoters, 5-Methylcytosine is associated with stable, long-term transcriptional silencing. This may occur by either blocking positive transcription factors, or promoting the binding of negative ones. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to 5-methylcytosine in both single-stranded and double-stranded DNA. No cross reactivity with non-methylated cytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA. Applications: DotBlot, MeDIP, ICC, ELISA, FC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. 5-Methylcytosine is a methylated form of the DNA base cytosine that regulates gene transcription and is involved in epigenetics. It is one of the best known epigentic modifications. This methylation typically occurs at cytosine in CpG dinucleotides in vertebrates. When cytosine is methylated, the DNA maintains the same sequence, but the expression of methylated genes can be altered. 5-Methylcytosine is a very important repressor of transcription in the genome. When present in promoters, 5-Methylcytosine is associated with stable, long-term transcriptional silencing. This may occur by either blocking positive transcription factors, or promoting the binding of negative ones.
- ReactivityVertebrate
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
