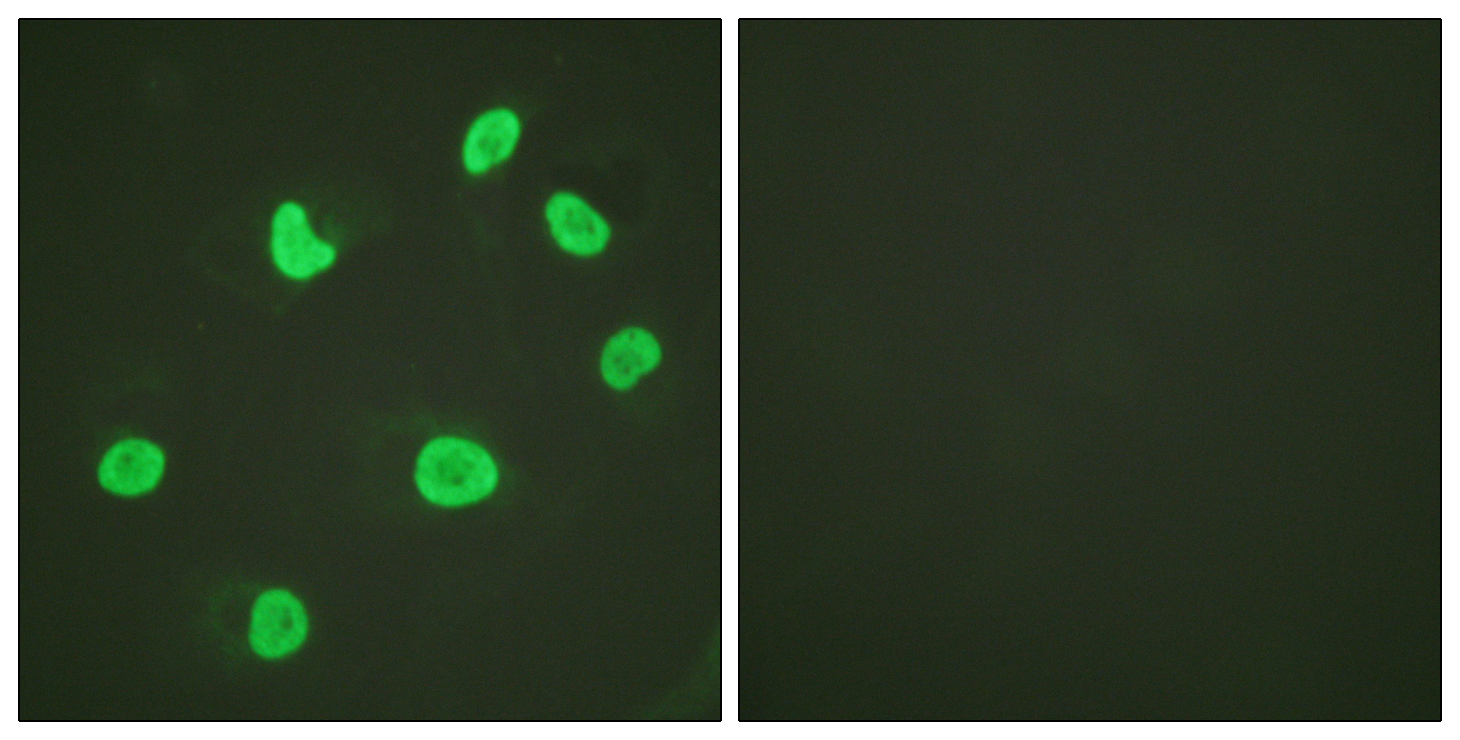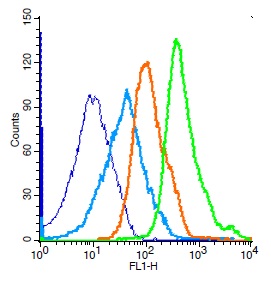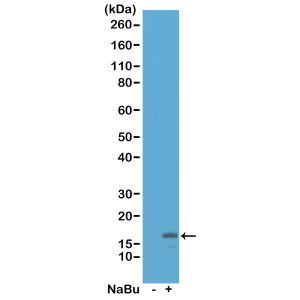
Western Blot of acid extracts from HeLa cells untreated (-) or treated with sodium butyrate (+), using RM166 at 0.5 ug/mL, showed a band of histone H3 acetylated at Lysine 18 in treated HeLa.
anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys18), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM166)
REV-31-1055-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityVertebrate
TargetH3-3A
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys18), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM166)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM166
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Gene ID3020
- Target nameH3-3A
- Target descriptionH3.3 histone A
- Target synonymsBRYLIB1, H3.3A, H3F3, H3F3A, histone H3.3, H3 histone family member 3A, H3 histone, family 3A
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP84243
- Protein NameHistone H3.3
- Scientific DescriptionHistone H3 is one of the DNA-binding proteins found in the chromatin of all eukaryotic cells. H3 along with four core histone proteins binds to DNA forming the structure of the nucleosome. Histones play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. Histone H3 has three main variants, H3.1 and H3.2, which are deposited in chromatin only during DNA replication and H3.3, which is replication independent and is found primarily in the regions of active transcription and heterochromatin. Post translationally, histones are modified in a variety of ways to either directly change the chromatin structure or allow for the binding of specific transcription factors. The N-terminal tail of histone H3 protrudes from the globular nucleosome core and can undergo several different types of post-translational modification that influence cellular processes. These modifications include the covalent attachment of methyl or acetyl groups to lysine and arginine amino acids and the phosphorylation of serine or threonine. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to Histone H3 acetylated at Lysine 18 (K18ac). No cross reactivity with other acetylated Lysines in histone H3. Applications: WB, ELISA, Multiplex, CHIP, ICC, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Histone H3 is one of the DNA-binding proteins found in the chromatin of all eukaryotic cells. H3 along with four core histone proteins binds to DNA forming the structure of the nucleosome. Histones play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. Histone H3 has three main variants, H3.1 and H3.2, which are deposited in chromatin only during DNA replication and H3.3, which is replication independent and is found primarily in the regions of active transcription and heterochromatin. Post translationally, histones are modified in a variety of ways to either directly change the chromatin structure or allow for the binding of specific transcription factors. The N-terminal tail of histone H3 protrudes from the globular nucleosome core and can undergo several different types of post-translational modification that influence cellular processes. These modifications include the covalent attachment of methyl or acetyl groups to lysine and arginine amino acids and the phosphorylation of serine or threonine.
- ReactivityVertebrate
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161