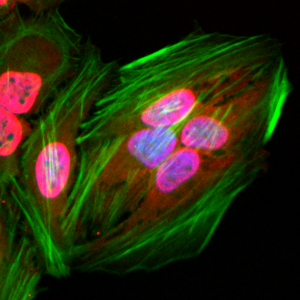
Immunocytochemical staining of HeLa cells using Anti-Acetylated Lysine antibody (RM101) (red). Actin filaments was labeled with fluorescein phalloidin (green), and nucleus stained with DAPI (blue).
anti-Acetylated-Lysine, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM101)
REV-32-1012-00
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityAll Species
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Acetylated-Lysine, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM101)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM101
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionAcetyllysine (or acetylated lysine) is an acetyl-derivative of the amino acid lysine. Post-translational acetylation occurs on the epsilon amino group of lysine residues as a reversible and highly dynamic post-translational modification (PTM) that is known to be a key regulator in multiple cellular events, including chromatin structure, transcription, metabolism, signal transduction and cytoskeletal regulation. The acetylation of lysine residues in proteins is an important mechanism of epigenetics. It functions by regulating the binding of histones to DNA in nucleosomes and thereby controlling the expression of genes on that DNA. Non-histone proteins are acetylated as well. Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) catalyze the addition of acetyl groups from acetyl-CoA onto certain lysine residues of histones and non-histone proteins. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) catalyze the removal of acetyl groups from acetylated lysines. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to lysine-acetylated proteins. No cross reactivity with nonacetylated lysine, and lysine with other modification. Applications: WB, IP, ICC, IHC, ELISA. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Acetyllysine (or acetylated lysine) is an acetyl-derivative of the amino acid lysine. Post-translational acetylation occurs on the epsilon amino group of lysine residues as a reversible and highly dynamic post-translational modification (PTM) that is known to be a key regulator in multiple cellular events, including chromatin structure, transcription, metabolism, signal transduction and cytoskeletal regulation. The acetylation of lysine residues in proteins is an important mechanism of epigenetics. It functions by regulating the binding of histones to DNA in nucleosomes and thereby controlling the expression of genes on that DNA. Non-histone proteins are acetylated as well. Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) catalyze the addition of acetyl groups from acetyl-CoA onto certain lysine residues of histones and non-histone proteins. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) catalyze the removal of acetyl groups from acetylated lysines.
- ReactivityAll Species
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
