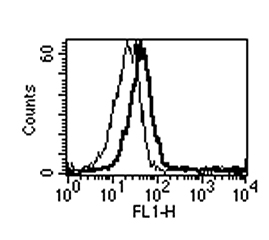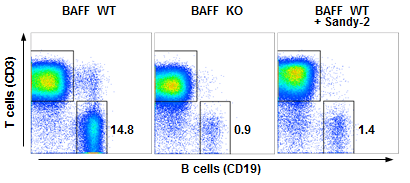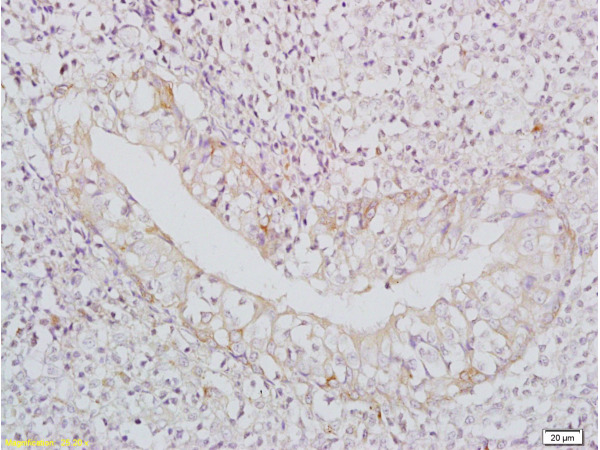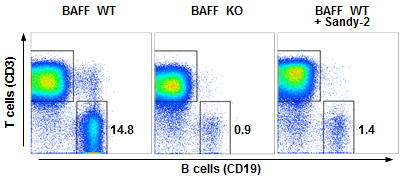
anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (Sandy-2) (preservative free) (Prod. No. AG-20B-0063PF) blocks the action of endogenous BAFF in vivo. Method: Wild type C57BL/6 mice were treated at day 0 (single administration) with monoclonal antibody anti-BA
anti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Sandy-2) (preservative free)
AG-20B-0063PF
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Neutralisation/Blocking
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityMouse
TargetTnfsf13b
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-BAFF (mouse), mAb (blocking) (Sandy-2) (preservative free)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Neutralisation/Blocking
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDSandy-2
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID24099
- Target nameTnfsf13b
- Target descriptiontumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b
- Target synonymsBAFF, BLyS, D8Ertd387e, TALL-1, TALL1, THANK, TNFSF20, Tnlg7a, zTNF4, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B, b cell-activating factor, tumor necrosis factor ligand 7a
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDQ9WU72
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B
- Scientific DescriptionBAFF is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival and, together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Increased levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases, such as Sjoegrens syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Furthermore, BAFF is found in inflammatory sites in which there is lymphoid neogenesis. BAFF levels are elevated in patients with multiple myeloma and B cell chronic lymphoid leukemia (B-CCL). - Monoclonal Antibody. Recognizes mouse BAFF. Isotype: Mouse IgG1. Clone: Sandy-2. Applications: FUNC (Blocking), IP. Liquid. In PBS containing 10% glycerol. BAFF is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival and, together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Increased levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases, such as Sjoegrens syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Furthermore, BAFF is found in inflammatory sites in which there is lymphoid neogenesis. BAFF levels are elevated in patients with multiple myeloma and B cell chronic lymphoid leukemia (B-CCL).
- ReactivityMouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161