Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human cervical squamous carcinoma tissue section using Anti-p16 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM409) at a 1:200 dilution.
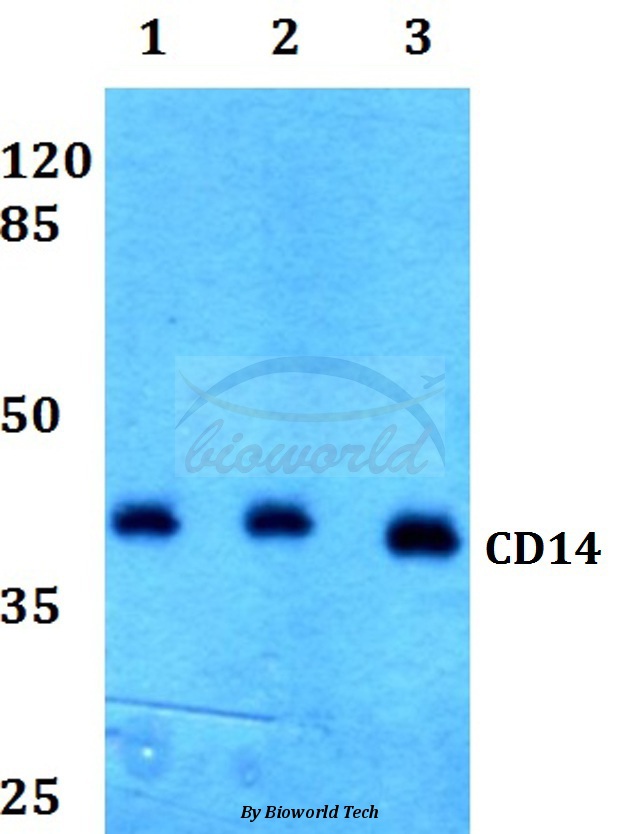
anti-CD14 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM415)
REV-31-1301-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD14
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD14 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM415)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM415
- Gene ID929
- Target nameCD14
- Target descriptionCD14 molecule
- Target synonymsmonocyte differentiation antigen CD14, my23 antigen, myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP08571
- Protein NameMonocyte differentiation antigen CD14
- Scientific DescriptionCD14 is a GPI-anchored glycoprotein that is constitutively expressed on the surface of mature monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and which is part of the innate immune system as a pattern recognition receptor. CD14 serves as a multifunctional lipopolysaccharide receptor together with TLR-4 and MD-2) and is released to the serum both as a secreted and enzymatically cleaved GPI-anchored form. CD14 binds lipopolysaccharide molecule in a reaction catalyzed by lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), an acute phase serum protein. The soluble sCD14 can discriminate slight structural differences between lipopolysaccharides and is important for neutralization of serum allochthonous lipopolysaccharides by reconstituted lipoprotein particles. Further, CD14 has been shown to bind apoptotic cells, and can affect allergic, inflammatory and infectious processes. Diseases associated with CD14 dysfunction include mycobacterium chelonae infection and croup. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human to CD14. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD14 is a GPI-anchored glycoprotein that is constitutively expressed on the surface of mature monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and which is part of the innate immune system as a pattern recognition receptor. CD14 serves as a multifunctional lipopolysaccharide receptor together with TLR-4 and MD-2) and is released to the serum both as a secreted and enzymatically cleaved GPI-anchored form. CD14 binds lipopolysaccharide molecule in a reaction catalyzed by lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), an acute phase serum protein. The soluble sCD14 can discriminate slight structural differences between lipopolysaccharides and is important for neutralization of serum allochthonous lipopolysaccharides by reconstituted lipoprotein particles. Further, CD14 has been shown to bind apoptotic cells, and can affect allergic, inflammatory and infectious processes. Diseases associated with CD14 dysfunction include mycobacterium chelonae infection and croup.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161