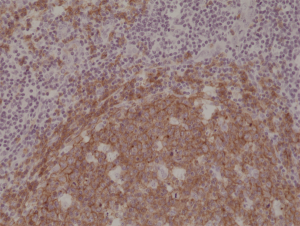
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human Tonsil tissue section using anti-CD19 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM332) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-CD19 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM332)
REV-31-1219-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD19
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD19 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM332)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM332
- Gene ID930
- Target nameCD19
- Target descriptionCD19 molecule
- Target synonymsB4, CVID3, B-lymphocyte antigen CD19, B-lymphocyte surface antigen B4, T-cell surface antigen Leu-12, differentiation antigen CD19
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP15391
- Protein NameB-lymphocyte antigen CD19
- Scientific DescriptionCD19 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and has two Ig like domains. The CD19 molecule is expressed on 100% of the peripheral B cells as defined by expression of kappa or lambda light chains. CD19 appears to be expressed on myeloid leukemia cells, particularly those of monocytic lineage. The receptor for CD19 is an important functional regulator of normal and malignant B cell proliferation, and is expressed in all B cell precursor leukemias. Lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate in response to various concentrations of different antigens. The ability of the B cell to respond in a specific, yet sensitive manner to the various antigens is achieved with the use of low-affinity antigen receptors. CD19 is a cell surface molecule which assembles with the antigen receptor of B lymphocytes in order to decrease the threshold for antigen receptor-dependent stimulation. Besides being a signal-amplifying coreceptor for the B cell receptor (BCR), CD19 can also signal independently of BCR co-ligation and is a central regulatory component upon which multiple signaling pathways converge. Mutation of the CD19 gene results in hypogammaglobulinemia, whereas CD19 overexpression causes B cell hyperactivity. CD19 is a biomarker for normal and neoplastic B cells, as well as follicular dendritic cells. CD19 is critically involved in establishing intrinsic B cell signaling thresholds through modulating both B cell receptor-dependent and independent signaling. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the cytoplasmic domain of human CD19. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD19 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and has two Ig like domains. The CD19 molecule is expressed on 100% of the peripheral B cells as defined by expression of kappa or lambda light chains. CD19 appears to be expressed on myeloid leukemia cells, particularly those of monocytic lineage. The receptor for CD19 is an important functional regulator of normal and malignant B cell proliferation, and is expressed in all B cell precursor leukemias. Lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate in response to various concentrations of different antigens. The ability of the B cell to respond in a specific, yet sensitive manner to the various antigens is achieved with the use of low-affinity antigen receptors. CD19 is a cell surface molecule which assembles with the antigen receptor of B lymphocytes in order to decrease the threshold for antigen receptor-dependent stimulation. Besides being a signal-amplifying coreceptor for the B cell receptor (BCR), CD19 can also signal independently of BCR co-ligation and is a central regulatory component upon which multiple signaling pathways converge. Mutation of the CD19 gene results in hypogammaglobulinemia, whereas CD19 overexpression causes B cell hyperactivity. CD19 is a biomarker for normal and neoplastic B cells, as well as follicular dendritic cells. CD19 is critically involved in establishing intrinsic B cell signaling thresholds through modulating both B cell receptor-dependent and independent signaling.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161








