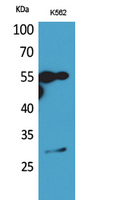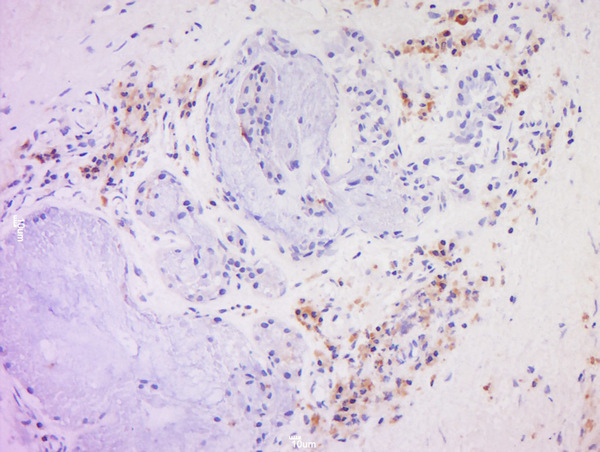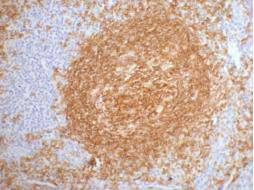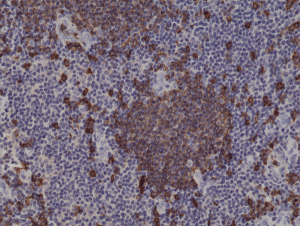
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human tonsil tissue sections using Anti-CD20 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM272) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-CD20 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM272)
REV-31-1153-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetMS4A1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD20 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM272)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM272
- Gene ID931
- Target nameMS4A1
- Target descriptionmembrane spanning 4-domains A1
- Target synonymsB1, Bp35, CD20, CVID5, FMC7, LEU-16, S7, B-lymphocyte antigen CD20, B-lymphocyte cell-surface antigen B1, CD20 antigen, CD20 receptor, leukocyte surface antigen Leu-16, membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP11836
- Protein NameB-lymphocyte antigen CD20
- Scientific DescriptionCD20 is a non-glycosylated surface phosphoprotein that has a molecular weight range of 33-37 kDa depending on the degree of phosphorylation. CD20 is expressed on mature and most malignant B cells, in a subpopulation of T lymphocytes and follicular dendritic cells. CD20 expression on B cells is synchronous with the expression of surface IgM and it regulates transmembrane calcium conductance, cell cycle progression and B cell proliferation. CD20 is also associated with lipid rafts, but the intensity of this association depends on extracellular triggering, employing CD20 conformational change, and/or BCR (B cell antigen receptor) aggregation. After the receptor ligation, BCR and CD20 colocalize and then rapidly dissociate before BCR endocytosis, whereas CD20 remains at the cell surface. CD20 serves as a useful target for antibody-mediated therapeutic depletion of B cells, as it is expressed at high levels on most B-cell malignancies, but does not become internalized or shed from the plasma membrane following monoclonal antibody treatment. Diseases associated with CD20 dysfunction include Ms4a1-related common variable immune deficiency, B cell non-Hodgkins lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the cytoplasmic domain of human CD20. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD20 is a non-glycosylated surface phosphoprotein that has a molecular weight range of 33-37 kDa depending on the degree of phosphorylation. CD20 is expressed on mature and most malignant B cells, in a subpopulation of T lymphocytes and follicular dendritic cells. CD20 expression on B cells is synchronous with the expression of surface IgM and it regulates transmembrane calcium conductance, cell cycle progression and B cell proliferation. CD20 is also associated with lipid rafts, but the intensity of this association depends on extracellular triggering, employing CD20 conformational change, and/or BCR (B cell antigen receptor) aggregation. After the receptor ligation, BCR and CD20 colocalize and then rapidly dissociate before BCR endocytosis, whereas CD20 remains at the cell surface. CD20 serves as a useful target for antibody-mediated therapeutic depletion of B cells, as it is expressed at high levels on most B-cell malignancies, but does not become internalized or shed from the plasma membrane following monoclonal antibody treatment. Diseases associated with CD20 dysfunction include Ms4a1-related common variable immune deficiency, B cell non-Hodgkins lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL).
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161