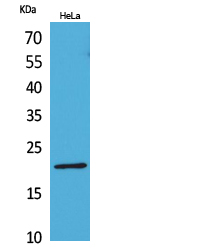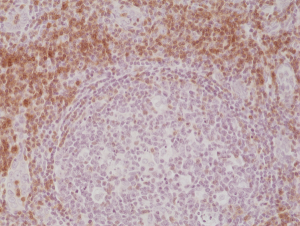
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human Tonsil tissue section using anti-CD3e rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM344) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-CD3E (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM344)
REV-31-1229-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD3E
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD3E (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM344)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM344
- Gene ID916
- Target nameCD3E
- Target descriptionCD3 epsilon subunit of T-cell receptor complex
- Target synonymsCD3epsilon, IMD18, T3E, TCRE, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain, CD3-epsilon, CD3e antigen, epsilon polypeptide (TiT3 complex), CD3e molecule, epsilon (CD3-TCR complex), T-cell antigen receptor complex, epsilon subunit of T3, T-cell surface antigen T3/Leu-4 epsilon chain
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP07766
- Protein NameT-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the cytoplasmic domain of human CD3 epsilon chain. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The CD3 subunit complex is crucial in transducing antigen-recognition signals into the cytoplasm of T cells and in regulating the cell surface expression of the TCR complex. T cell activation through the antigen receptor (TCR) involves the cytoplasmic tails of the CD3 subunits CD3 gamma, CD3 delta, CD3 epsilon and CD3 zeta. The CD3 components have long cytoplasmic tails that associate with cytoplasmic signal transduction molecules and this association is mediated at least in part by a double tyrosine-based motif present in a single copy in the CD3 subunits. CD3 may play a role in TCR-induced growth arrest, cell survival and proliferation. The CD3 antigen is present on 68-82% of normal peripheral blood lymphocytes, 65-85% of thymocytes and Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, but it is not expressed on B or NK cells. T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain has been shown to interact with TOP2B, CD3EAP and NCK2. - The CD3 subunit complex is crucial in transducing antigen-recognition signals into the cytoplasm of T cells and in regulating the cell surface expression of the TCR complex. T cell activation through the antigen receptor (TCR) involves the cytoplasmic tails of the CD3 subunits CD3 gamma, CD3 delta, CD3 epsilon and CD3 zeta. The CD3 components have long cytoplasmic tails that associate with cytoplasmic signal transduction molecules and this association is mediated at least in part by a double tyrosine-based motif present in a single copy in the CD3 subunits. CD3 may play a role in TCR-induced growth arrest, cell survival and proliferation. The CD3 antigen is present on 68-82% of normal peripheral blood lymphocytes, 65-85% of thymocytes and Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, but it is not expressed on B or NK cells. T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain has been shown to interact with TOP2B, CD3EAP and NCK2.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161