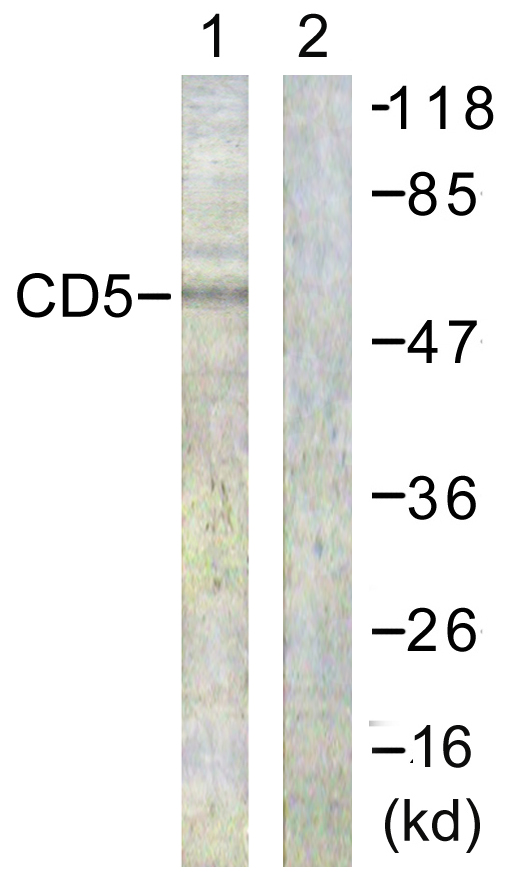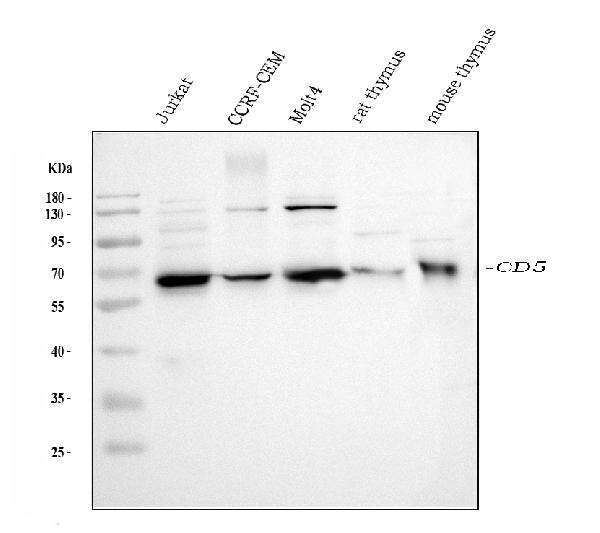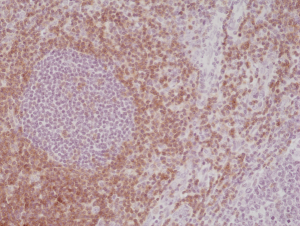
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human tonsil tissue section using anti-CD5 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM354) at a 1:500 dilution.
anti-CD5 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM354)
REV-31-1240-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD5
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD5 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM354)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM354
- Gene ID921
- Target nameCD5
- Target descriptionCD5 molecule
- Target synonymsLEU1, T1, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD5, CD5 antigen (p56-62), epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, lymphocyte antigen T1/Leu-1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP06127
- Protein NameT-cell surface glycoprotein CD5
- Scientific DescriptionCD5 is a 67 kDa human T-lymphocyte single-chain transmembrane glycoprotein. CD5 serves to mitigate activating signals from the BCR so that the B-1 cells can only be activated by very strong stimuli (such as bacterial proteins) and not by normal tissue proteins. CD5 is present on all mature T-lymphocytes, on most of thymocytes and on many T-cell leukemias and lymphomas. CD5 also reacts with a subpopulation of activated B-cells and may act as a receptor in regulating T-cell proliferation. CD5 is found on 95% of thymocytes and 72% of peripheral blood lymphocytes. In lymph nodes, the main reactivity is observed in T cell areas. CD5 is expressed by many T cell leukemia, lymphomas and activated T cells. Diseases associated with CD5 dysfunction include thymus cancer and Richters Syndrome. CD5 is a good immunohistochemical marker for T-cells, although not as sensitive as CD3. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CD5 . Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD5 is a 67 kDa human T-lymphocyte single-chain transmembrane glycoprotein. CD5 serves to mitigate activating signals from the BCR so that the B-1 cells can only be activated by very strong stimuli (such as bacterial proteins) and not by normal tissue proteins. CD5 is present on all mature T-lymphocytes, on most of thymocytes and on many T-cell leukemias and lymphomas. CD5 also reacts with a subpopulation of activated B-cells and may act as a receptor in regulating T-cell proliferation. CD5 is found on 95% of thymocytes and 72% of peripheral blood lymphocytes. In lymph nodes, the main reactivity is observed in T cell areas. CD5 is expressed by many T cell leukemia, lymphomas and activated T cells. Diseases associated with CD5 dysfunction include thymus cancer and Richters Syndrome. CD5 is a good immunohistochemical marker for T-cells, although not as sensitive as CD3.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161