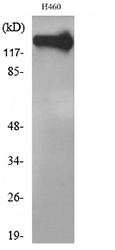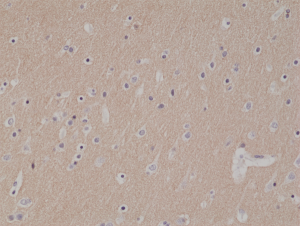
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human brain tissue section using anti-CD56 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM315) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-CD56 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM315)
REV-31-1201-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetNCAM1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD56 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM315)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM315
- Gene ID4684
- Target nameNCAM1
- Target descriptionneural cell adhesion molecule 1
- Target synonymsCD56, MSK39, NCAM, neural cell adhesion molecule 1, antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody 5.1H11, neural cell adhesion molecule, NCAM
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP13591
- Protein NameNeural cell adhesion molecule 1
- Scientific DescriptionCD56 (NCAM; Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule) is a transmembrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin family that serves as an adhesive molecule and is ubiquitously expressed in the nervous system in isoforms ranging from 120-180 kDa. CD56 is found on T cells and NK cells, and is involved in cell migration, axonal growth, pathfinding and synaptic plasticity. Polysialic modification results in reduction of CD56-mediated cell adhesion. Through its extracellular region, CD56 mediates homophilic and heterophilic interactions by binding extracellular matrix components such as laminin and integrins. CD56 is expressed on most neuroectodermal derived cell lines, tissues and neoplasms such as retinoblastoma, medulloblastoma, astrocytomas and neuroblastoma. CD56 is a widely used neuroendocrine marker with a high sensitivity for neuroendocrine tumors and ovarian granulosa cell tumors. Diseases associated with CD56 dysfunction include rabies and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CD56 (NCAM1). It may also react to mouse CD56, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD56 (NCAM; Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule) is a transmembrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin family that serves as an adhesive molecule and is ubiquitously expressed in the nervous system in isoforms ranging from 120-180 kDa. CD56 is found on T cells and NK cells, and is involved in cell migration, axonal growth, pathfinding and synaptic plasticity. Polysialic modification results in reduction of CD56-mediated cell adhesion. Through its extracellular region, CD56 mediates homophilic and heterophilic interactions by binding extracellular matrix components such as laminin and integrins. CD56 is expressed on most neuroectodermal derived cell lines, tissues and neoplasms such as retinoblastoma, medulloblastoma, astrocytomas and neuroblastoma. CD56 is a widely used neuroendocrine marker with a high sensitivity for neuroendocrine tumors and ovarian granulosa cell tumors. Diseases associated with CD56 dysfunction include rabies and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161