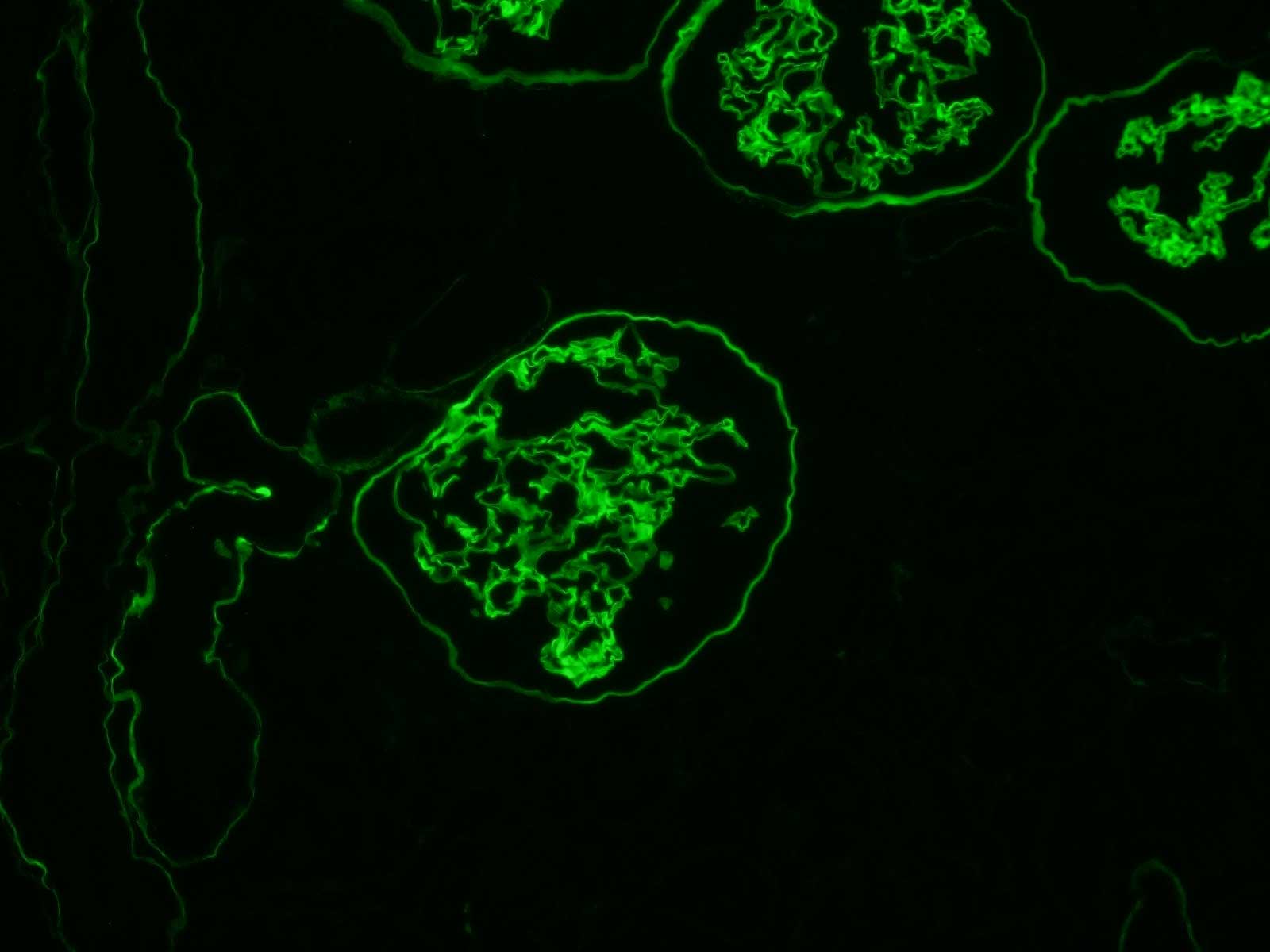
Anti Collagen 4 (ALPHA)5(IV) mAb (Clone H53, Fluorescein Labeled)
SGE-CFT453
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence
Product group Antibodies
Overview
- SupplierCosmo Bio USA
- Product NameAnti Collagen 4 (ALPHA)5(IV) mAb (Clone H53, Fluorescein Labeled)
- Delivery Days Customer16
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDClone h53
- ConjugateFITC
- HostRat
- Scientific DescriptionCheck out our Human Collagen IValpha Rat Monoclonal Antibodies Dashboard for more information about this product and additional epitope-defined monoclonal antibodies useful for research on hereditary diseases related to collagen IV, including our popular Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25) (SGE-CFT45325). Alport syndrome is an inherited disease characterized by the pathological absence or reduction of the collagen alpha5(IV) chain in glomerular basement membrane (GBM), tubular basement membrane (TBM) and Bowmans capsular basement membrane. Anti Collagen 4 (ALPHA)5(IV) mAb (Clone H53, Fluorescein Labeled) (cat no. SGE-CFT453) is one of three different rat mAbs included in Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25) (SGE-CFT45325) for easy and rapid staining of human renal and skin biopsy sections to distinguish Alport syndrome from normal tissue. Anti-Collagen 4 Cocktail mAb (Clones H53, B51, H25) comprises two different FITC-conjugated mAbs (clones H53 and B51) that reveal the Alport-affected alpha5(IV) chain in glomerular, tubular and Bowmans capsular BMs and an internal positive control Texas Red-conjugated mAb (clone H25) that targets alpha2(IV) to reveal endothelial basement membrane structure Product specifications References Kagawa M et al. Epitope-defined monoclonal antibodies against type-IV collagen for diagnosis of Alport syndrome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 12: 1238-1241 (1997) (PMID: 9198058) Borza DB et al. The NCI domain of collagen IV encodes a novel network composed of the alpha1, alpha2, alpha5, and alpha6 chains in smooth muscle basement membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 28532-28540 (2001) (PMID: 11375996) Sado et al. Establishment by the rat lymph node method of epitope-defined monoclonal antibodies recognizing the six different alpha chains of human type IV collagen. Histochem. Cell Biol. 104: 267-275 (1995) (PMID: 8548560) Yoshioka K et al. Type IV collagen alpha5 chain: Normal distribution and abnormalities in X-linked Alport syndrome revealed by monoclonal antibody. Am. J. Pathol. 144: 986-996 (1994) (PMID: 8178947) Ninomiya Y et al. Differential expression of two basement membrane collagen genes, COL4A6 and COL4A5, demonstrated by immunofluorescence staining using peptide-specific monoclonal antibodies. J. Cell Biol. 130: 1219-1229 (1995) (PMID: 7657706) Naito I et al. Relationship between COL4A5 gene mutation and distribution of type IV collagen in male X-linked Alport syndrome. Kidney Int. 50: 304-311 (1996) (PMID: 8807602) Citations Bu L et al. Somatic Mosaicism in a Male Patient With X-linked Alport Syndrome. Kidney Int Rep. 14(4): 1031-1035 (2019) (PMID: 31312776) Samar M et al. Negative Staining for COL4A5 Correlates With Worse Prognosis and More Severe Ultrastructural Alterations in Males With Alport Syndrome. Kidney Int Rep. 2(1): 44-52 (2017) (PMID: 29142939) Malone AF et al. Functional assessment of a novel COL4A5 splice region variant and immunostaining of plucked hair follicles as an alternative method of diagnosis in X-linked Alport syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 32(6): 997-1003 (2017) (PMID: 28013382) Nozu K et al. X-linked Alport syndrome caused by splicing mutations in COL4A5. Am Soc Nephrol. 9(11): 1958-64 (2014) (PMID: 25183659) Matsubara S et al. Pregnancy complicated with Alport syndrome: a good obstetric outcome and failure to diagnose an infant born to a mother with Alport syndrome by umbilical cord immunofluorescence staining. Obstet Gynaecol Res. 35(6): 1109-14 (2009) (PMID: 20144175) Patey-Mariaud de Serre N et al. Collagen alpha5 and alpha2(IV) chain coexpression: analysis of skin biopsies of Alport patients. Kidney Int. 72(4): 512-6 (2007) (PMID: 17554254) Kharrat M et al. Autosomal dominant Alports syndrome: study of a large Tunisian family. Kidney Dis Transpl. 17(3): 320-5 (2006) (PMID: 16970251)
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
