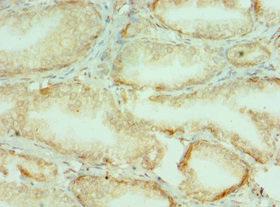
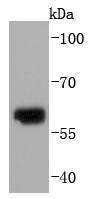
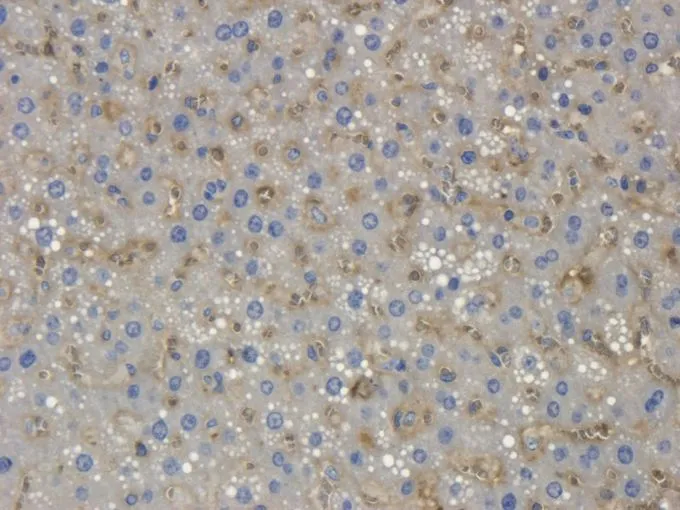
Western blot analysis of Collagen X expression in human fetal skin lysate.
Anti-Collagen X COL10A1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
M01026
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCOL10A1
Overview
- SupplierBoster Bio
- Product NameAnti-Collagen X COL10A1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDAOAH-3
- Gene ID1300
- Target nameCOL10A1
- Target descriptioncollagen type X alpha 1 chain
- Target synonymscollagen alpha-1(X) chain, Schmid metaphyseal chondrodysplasia, collagen X, alpha-1 polypeptide, collagen, type X, alpha 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ03692
- Protein NameCollagen alpha-1(X) chain
- Scientific DescriptionBoster Bio Anti-Collagen X COL10A1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody catalog # M01026. Tested in WB application. This antibody reacts with Human, Mouse, Rat.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Gao Y, Wang J, Dai W, et al. Collagen-based hydrogels induce hyaline cartilage regeneration by immunomodulation and homeostasis maintenance. Acta Biomater. 2024,186:108-124. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.07.018Read this paper
- Wang W, Ma Z, Feng X, et al. TfR1 mediated iron metabolism dysfunction as a potential therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024,26(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03304-xRead this paper
- Zhu Y, Sun Y, Rui B, et al. A Photoannealed Granular Hydrogel Facilitating Hyaline Cartilage Regeneration via Improving Chondrogenic Phenotype. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022,14(36):40674-40687. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c11956Read this paper