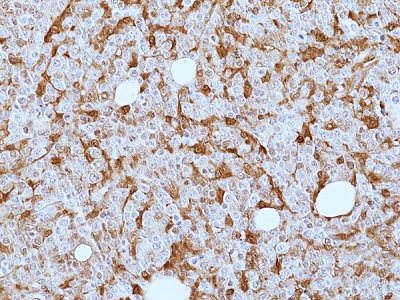
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human diffuse large B cell lymphoma tissue sections using anti-Galectin-9 antibody (RM499) at 1:200 dilution.
anti-Galectin-9 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM499)
REV-31-1391-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetLGALS9
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Galectin-9 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM499)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM499
- Gene ID3965
- Target nameLGALS9
- Target descriptiongalectin 9
- Target synonymsHUAT, LGALS9A, galectin-9, ecalectin, gal-9, lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 9, tumor antigen HOM-HD-21, urate transporter/channel protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO00182
- Protein NameGalectin-9
- Scientific DescriptionGalectin-9 (Gal-9), a beta-galactoside-binding protein, primarily plays an immunosuppressive role in the tumor microenvironment, via binding with several cell surface receptors expressed on immune cells. Although Gal-9 was initially identified as a ligand for T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing molecule 3 (TIM-3) in the induction of T-cell death, it also binds to other immunoregulatory receptors. For instance, Gal-9 binding to the innate receptor dectin-1 promotes M2 polarization of macrophages that suppresses antitumor immune responses. Gal-9 has also been shown to promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) through interaction with cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) and drive the expansion of Tregs through binding with death receptor 3. The aberrantly high expression of Gal-9 in a range of cancers suggests that Gal-9 could be significant both as a biomarker and a therapeutic target. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Galectin-9. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: A peptide corresponding to the N-terminus of human Galectin-9 (Gal-9). Application: IHC, WB. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Galectin-9 (Gal-9), a beta-galactoside-binding protein, primarily plays an immunosuppressive role in the tumor microenvironment, via binding with several cell surface receptors expressed on immune cells. Although Gal-9 was initially identified as a ligand for T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing molecule 3 (TIM-3) in the induction of T-cell death, it also binds to other immunoregulatory receptors. For instance, Gal-9 binding to the innate receptor dectin-1 promotes M2 polarization of macrophages that suppresses antitumor immune responses. Gal-9 has also been shown to promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) through interaction with cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) and drive the expansion of Tregs through binding with death receptor 3. The aberrantly high expression of Gal-9 in a range of cancers suggests that Gal-9 could be significant both as a biomarker and a therapeutic target.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161








