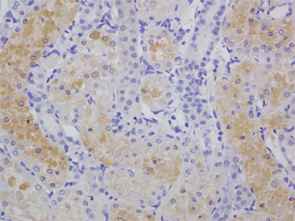
Immunohistochemical staining of cisplatin-treated rat kidney using anti-HEL, mAb (5F12).
anti-Hexanoyl-Lys [HEL], mAb (5F12)
JAI-MHL-021P
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityAll Species, Human
Overview
- SupplierJaICA
- Product Nameanti-Hexanoyl-Lys [HEL], mAb (5F12)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID5F12
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Scientific DescriptionMonoclonal Antibody. Recognizes Hexanoyl-Lys adducts. Does not cross-react with MDA, glyoxal, methylglyoxal, 1-hexanal, 2-hexenal, 1-nonannal, 2-nonenal, 4-hudroxy-2-nonenal. Lyophilized. Contains 10mM PBS (pH7.4), 5% sucrose, 1% BSA and 0.05% Procline 950. Oxidative damage to lipids (lipid peroxidation) has been found to play an important role in various disease and aging processes. During early stages of lipid peroxidation, lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) are formed. These can react additionally to form later stage end products such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydroxynonenal (HNE). LOOH is measured to quantify early stage or acute lipid peroxidation while MDA is commonly measured to quantify late stage or chronic lipid peroxidation. More recently, it has been reported that 13-hydroperoxyoctadecanoic acid (13-HPODE), a precursor to 13-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid (13-HODE) can react with proteins to form measurable adducts by covalently binding to specific amino acid residues. The Hexanoyl-Lysine (HEL) adduct is formed upon oxidative modification of omega-6 fatty acids such as linoleic acid, the predominant polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) in the human diet, and arachidonic acid. HEL may be another useful biomarker for detecting and quantifying the earlier stages of lipid peroxidation. - Oxidative damage to lipids (lipid peroxidation) has been found to play an important role in various disease and aging processes. During early stages of lipid peroxidation, lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) are formed. These can react additionally to form later stage end products such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydroxynonenal (HNE). LOOH is measured to quantify early stage or acute lipid peroxidation while MDA is commonly measured to quantify late stage or chronic lipid peroxidation. More recently, it has been reported that 13-hydroperoxyoctadecanoic acid (13-HPODE), a precursor to 13-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid (13-HODE) can react with proteins to form measurable adducts by covalently binding to specific amino acid residues. The Hexanoyl-Lysine (HEL) adduct is formed upon oxidative modification of omega-6 fatty acids such as linoleic acid, the predominant polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) in the human diet, and arachidonic acid. HEL may be another useful biomarker for detecting and quantifying the earlier stages of lipid peroxidation.
- ReactivityAll Species, Human
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
