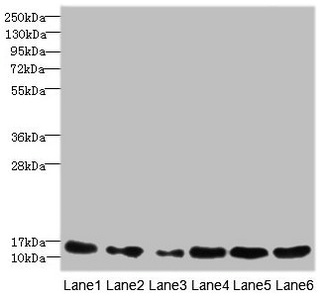
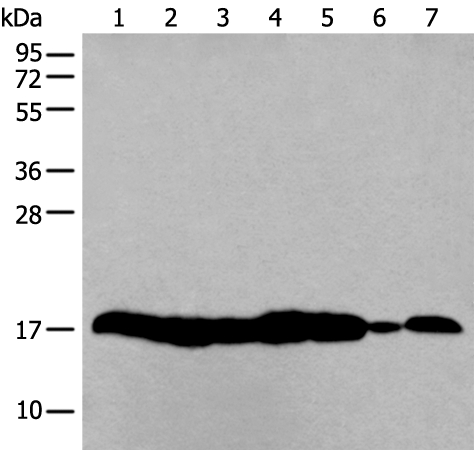
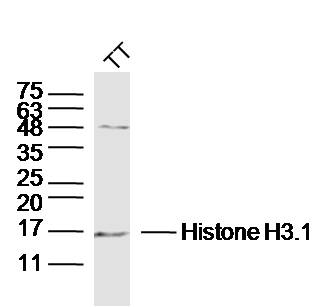
All lanes use the Antibody at 1:5K dilution for 1 hour at room temperature.
Anti-Histone H3 HIST1H3A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
M12477-10
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetH3C1
Overview
- SupplierBoster Bio
- Product NameAnti-Histone H3 HIST1H3A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDHDE-8
- Gene ID8350
- Target nameH3C1
- Target descriptionH3 clustered histone 1
- Target synonymsH3/A, H3C10, H3C11, H3C12, H3C2, H3C3, H3C4, H3C6, H3C7, H3C8, H3FA, HIST1H3A, histone H3.1, H3 histone family, member A, histone 1, H3a, histone H3/a, histone cluster 1 H3 family member a, histone cluster 1, H3a
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP68431
- Protein NameHistone H3.1
- Scientific DescriptionBoster Bio Anti-Histone H3 HIST1H3A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody catalog # M12477-10. Tested in WB, IHC, ICC/IF applications. This antibody reacts with Human, Mouse, Rat.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Zhu J, Cheng W, He TT, et al. Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Tryptanthrin by Regulating TLR4/MyD88/ROS/NF-κB, JAK/STAT3, and Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways. ACS Omega. 2024,9(28):30904-30918. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03795Read this paper
- Liu H, Wang X, He K, et al. Oxidized DJ-1 activates the p-IKK/NF-κB/Beclin1 pathway by binding PTEN to induce autophagy and exacerbate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024,971:176496. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176496Read this paper
- Yan X, Lin T, Zhu Q, et al. Naringenin protects against acute pancreatitis-associated intestinal injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via AhR signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2023,14:1090261. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1090261Read this paper
- Yu Q, Liu JX, Zheng X, et al. Sox9 mediates autophagy-dependent vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation and transplant arteriosclerosis. iScience. 2022,25(10):105161. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105161Read this paper
- Zhou J, Ni W, Ling Y, et al. Human Neural Stem Cell Secretome Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation Through Modulating Microglia Polarization by Activating Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma. Stem Cells Dev. 2022,31(13-14):369-382. doi: 10.1089/scd.2022.0081Read this paper
- Yu Q, Li W, Xie D, et al. PI3Kγ promotes vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation and transplant arteriosclerosis via a SOX9-dependent mechanism. EBioMedicine. 2018,36:39-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.013Read this paper