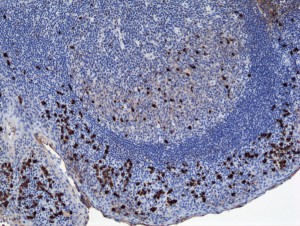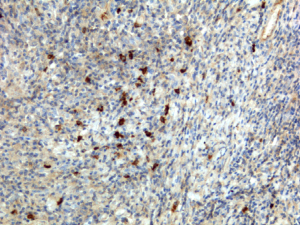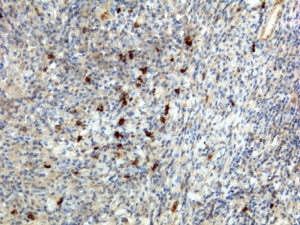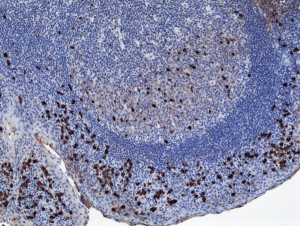
Immunohistochemistry of Human Tonsil Tissue using Anti-Human IgA1 antibody RM124.
anti-IgA1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM124)
REV-31-1026-00
ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-IgA1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM124)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM124
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01876
- Protein NameImmunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1
- Scientific DescriptionImmunoglobulin A (IgA) is an antibody isotype that plays a crucial role in the immune function of mucous membranes. IgA has two subclasses (IgA1 and IgA2) and can be produced as a monomeric as well as a dimeric form. The IgA dimeric form is the most prevalent and is also called secretory IgA (sIgA). sIgA is the main immunoglobulin found in mucous secretions, including tears, saliva, sweat, colostrum and secretions from the genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, prostate and respiratory epithelium. It is also found in small amounts in blood. The secretory component of sIgA protects the immunoglobulin from being degraded by proteolytic enzymes; thus, sIgA can survive in the harsh gastrointestinal tract environment and provide protection against microbes that multiply in body secretions. In the blood, IgA interacts with the Fc receptor called FcalphaRI (or CD89), which is expressed on immune effector cells, to initiate inflammatory reactions. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgA1 immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human IgA1, and very slightly cross reacts with IgA2. No cross reactivity with human IgG, IgM, IgD, or IgE. Applications: ICC, IHC, ELISA. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is an antibody isotype that plays a crucial role in the immune function of mucous membranes. IgA has two subclasses (IgA1 and IgA2) and can be produced as a monomeric as well as a dimeric form. The IgA dimeric form is the most prevalent and is also called secretory IgA (sIgA). sIgA is the main immunoglobulin found in mucous secretions, including tears, saliva, sweat, colostrum and secretions from the genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, prostate and respiratory epithelium. It is also found in small amounts in blood. The secretory component of sIgA protects the immunoglobulin from being degraded by proteolytic enzymes; thus, sIgA can survive in the harsh gastrointestinal tract environment and provide protection against microbes that multiply in body secretions. In the blood, IgA interacts with the Fc receptor called FcalphaRI (or CD89), which is expressed on immune effector cells, to initiate inflammatory reactions. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgA1 immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161