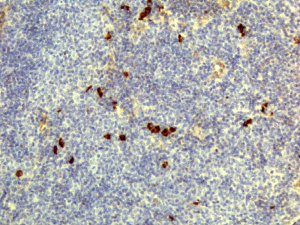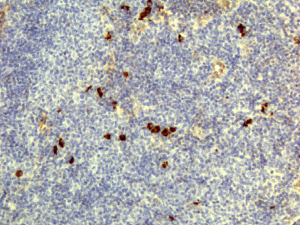
Immunohistochemistry of Human Lymphoid Tissue using Anti-Human IgD antibody RM123.
anti-IgD (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM123)
REV-31-1025-00
ApplicationsELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-IgD (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM123)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM123
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01880
- Protein NameImmunoglobulin heavy constant delta
- Scientific DescriptionImmunoglobulin D (IgD) is an antibody isotype that makes up about 1% of proteins in the plasma membranes of immature B-lymphocytes where it is usually co-expressed with IgM. IgD is also produced in a secreted form that is found in very small amounts in blood serum, representing 0.25% of immunoglobulins in serum. Secreted IgD is produced as a monomeric antibody with two heavy chains of the delta (delta) class, and two Ig light chains. In B cells, the function of IgD is to signal the B cells to be activated. By being activated, B cells are ready to take part in the defense of the body as part of the immune system. IgD was found to bind to basophils and mast cells and activate these cells to produce antimicrobial factors to participate in respiratory immune defense in humans. It also stimulates basophils to release B cell homeostatic factors. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgD immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human IgD. No cross reactivity with human IgG, IgM, IgA, or IgE. Applications: ELISA. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is an antibody isotype that makes up about 1% of proteins in the plasma membranes of immature B-lymphocytes where it is usually co-expressed with IgM. IgD is also produced in a secreted form that is found in very small amounts in blood serum, representing 0.25% of immunoglobulins in serum. Secreted IgD is produced as a monomeric antibody with two heavy chains of the delta (delta) class, and two Ig light chains. In B cells, the function of IgD is to signal the B cells to be activated. By being activated, B cells are ready to take part in the defense of the body as part of the immune system. IgD was found to bind to basophils and mast cells and activate these cells to produce antimicrobial factors to participate in respiratory immune defense in humans. It also stimulates basophils to release B cell homeostatic factors. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgD immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161