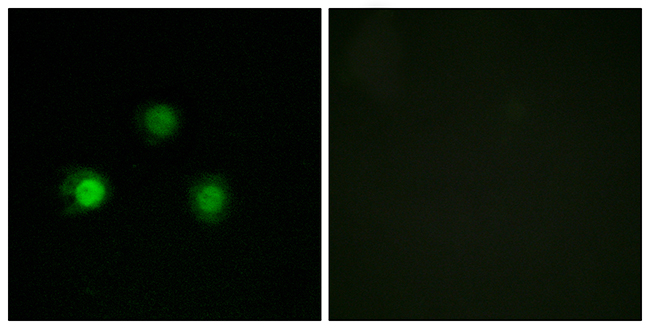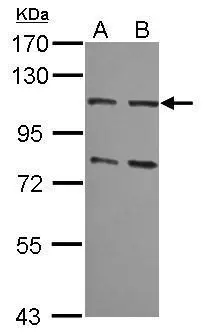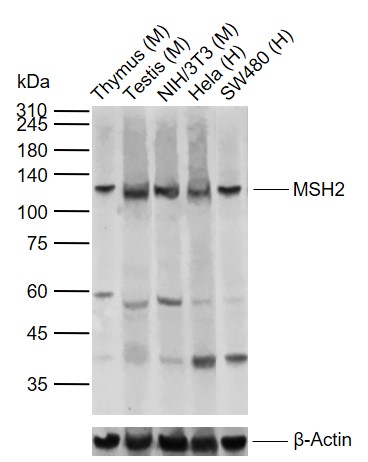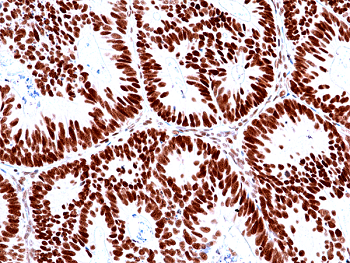
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human colon cancer tissues with MSH2 expression, using anti-MSH2 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM478) at a 1:100 dilution.
anti-MSH2 (C-Term) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM478)
REV-31-1370-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetMSH2
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-MSH2 (C-Term) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM478)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM478
- Gene ID4436
- Target nameMSH2
- Target descriptionmutS homolog 2
- Target synonymsCOCA1, FCC1, HNPCC, HNPCC1, LCFS2, LYNCH1, MMRCS2, MSH-2, hMSH2, DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2, DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 transcript, MutS-like 2, mutS homolog 2, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP43246
- Protein NameDNA mismatch repair protein Msh2
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human DNA mismatch repair protein MSH2. Source: Rabbit. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: Recombinant protein within 500 amino acids of the C-terminus of human MSH2. Applications: IHC, WB. The mismatch repair (MMR) proteins are required to maintain genomic integrity in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, by correcting single mismatches and short unpaired regions, such as small insertions and deletions. In eukaryotes, three proteins are involved in mismatch recognition, MSH2, MSH3 and MSH6. The three proteins form two heterodimers MutSalpha (MSH2-MSH6) and MutSbeta (MSH2-MSH3). MutSalpha is thought to be involved primarily in the recognition and repair of base-base mismatches and small insertion/deletion loops. MutSbeta acts preferentially on insertion/deletion loops up to 12 nucleotides in length. The MSH2, MSH3, and PMS2 mismatch repair proteins are also involved in other DNA repair pathways such as single-strand annealing and homologous recombination, anti-recombination, DNA damage signaling, apoptosis, as well as site-specific mutagenesis during immunoglobin somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination. They interact with several other oncogenic targets, including ATR, BRCA1 or p53. Deficiencies in expression of DNA repair genes underlie many forms of cancer. If DNA repair is deficient, DNA damage tends to accumulate. Such excess DNA damage may increase mutations due to error-prone translesion synthesis and error prone repair. Elevated DNA damage may also increase epigenetic alterations due to errors during DNA repair. Such mutations and epigenetic alterations may give rise to cancer. MSH2 mutation is a commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). MSH2 mutations have also been linked to endometrial cancer and the development of endometrial carcinomas. - The mismatch repair (MMR) proteins are required to maintain genomic integrity in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, by correcting single mismatches and short unpaired regions, such as small insertions and deletions. In eukaryotes, three proteins are involved in mismatch recognition, MSH2, MSH3 and MSH6. The three proteins form two heterodimers MutSalpha (MSH2-MSH6) and MutSbeta (MSH2-MSH3). MutSalpha is thought to be involved primarily in the recognition and repair of base-base mismatches and small insertion/deletion loops. MutSbeta acts preferentially on insertion/deletion loops up to 12 nucleotides in length. The MSH2, MSH3, and PMS2 mismatch repair proteins are also involved in other DNA repair pathways such as single-strand annealing and homologous recombination, anti-recombination, DNA damage signaling, apoptosis, as well as site-specific mutagenesis during immunoglobin somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination. They interact with several other oncogenic targets, including ATR, BRCA1 or p53. Deficiencies in expression of DNA repair genes underlie many forms of cancer. If DNA repair is deficient, DNA damage tends to accumulate. Such excess DNA damage may increase mutations due to error-prone translesion synthesis and error prone repair. Elevated DNA damage may also increase epigenetic alterations due to errors during DNA repair. Such mutations and epigenetic alterations may give rise to cancer. MSH2 mutation is a commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). MSH2 mutations have also been linked to endometrial cancer and the development of endometrial carcinomas.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161