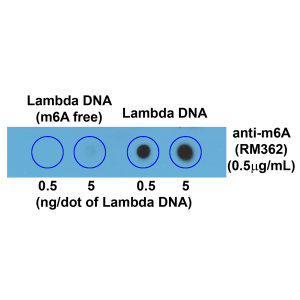
Dot blot of Lambda DNA without or with m6A, using anti-m6A antibody (RM362). The membrane was pre-spotted with 5, and 0.5 ng/dot of lambda DNA. m6A-free DNA was isolated from bacteriophage lambda grown in an E. coli host-deficient in adenine methylase (da
anti-N6-Methyladenosine, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM362)
REV-31-1248-00
ApplicationsDot Blot, ELISA, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityAll Species
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-N6-Methyladenosine, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM362)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsDot Blot, ELISA, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM362
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionN6-methyladenosine (m6A) is methylation that occurs in the N6-position of adenosine, which is the most prevalent internal modification on eukaryotic mRNA. Accumulating evidence suggests that m6A modulates gene expression, thereby regulating cellular processes ranging from cell self-renewal, differentiation, invasion and apoptosis. M6A is installed by m6A methyltransferases, removed by m6A demethylases and recognized by reader proteins, which regulate of RNA metabolism including translation, splicing, export, degradation and microRNA processing. Alteration of m6A levels participates in cancer pathogenesis and development via regulating expression of tumor-related genes like BRD4, MYC, SOCS2 and EGFR. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in both RNA and DNA. No cross reactivity with non-methylated adenosine. Applications: DotBlot, ELISA, MeRIP. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is methylation that occurs in the N6-position of adenosine, which is the most prevalent internal modification on eukaryotic mRNA. Accumulating evidence suggests that m6A modulates gene expression, thereby regulating cellular processes ranging from cell self-renewal, differentiation, invasion and apoptosis. M6A is installed by m6A methyltransferases, removed by m6A demethylases and recognized by reader proteins, which regulate of RNA metabolism including translation, splicing, export, degradation and microRNA processing. Alteration of m6A levels participates in cancer pathogenesis and development via regulating expression of tumor-related genes like BRD4, MYC, SOCS2 and EGFR.
- ReactivityAll Species
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
