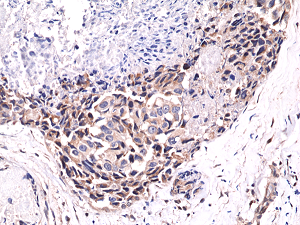
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue sections using Anti-Phospho-Akt (Ser473) RM251 at a 1:400 dilution.
anti-Phospho-Akt (Ser473) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM251)
REV-31-1131-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetAKT1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Phospho-Akt (Ser473) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM251)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM251
- Gene ID207
- Target nameAKT1
- Target descriptionAKT serine/threonine kinase 1
- Target synonymsAKT, PKB, PKB-ALPHA, PRKBA, RAC, RAC-ALPHA, RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase, AKT1m, PKB alpha, RAC-PK-alpha, protein kinase B alpha, proto-oncogene c-Akt, rac protein kinase alpha, serine-threonine protein kinase, v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1, v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene-like protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP31749
- Protein NameRAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase
- Scientific DescriptionAkt, also referred to as PKB or Rac, plays a critical role in controlling survival and apoptosis. This protein kinase is activated at 2 phosphorylation sites Thr308 and Ser473. Akt promotes cell survival by inhibiting apoptosis through phosphorylation and inactivation of several targets, including Bad, forkhead transcription factors, c-Raf and caspase-9. In addition to its role in survival and glycogen synthesis, Akt is involved in cell cycle regulation. Akt also plays a critical role in cell growth by directly phosphorylating mTOR in a rapamycin-sensitive complex containing raptor. Mutation of the glutamic acid at residue 17 to lysine (E17K) of Akt was initially identified in human breast, colorectal and ovarian cancers. This conserved glutamic acid residue is located at the lipid-binding pocket of the Akt plextrin homology domain. The E17K mutation increases the affinity between Akt and phospholipids at the plasma membrane, leading to increased Akt recruitment, super-activation of the Akt pathway, cellular transformation and tumor formation. Additional studies detect the presence of the Akt (E17K) mutation in multiple cancers, including lung cancer, prostate cancer, endometrial carcinoma and several melanomas. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to Akt only when phosphorylated at Ser473. There is no cross-reactivity with Akt without phosphorylation at Ser473. This antibody may also react to bovine, mouse or rat Phospho-Akt (Ser473), as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Akt, also referred to as PKB or Rac, plays a critical role in controlling survival and apoptosis. This protein kinase is activated at 2 phosphorylation sites Thr308 and Ser473. Akt promotes cell survival by inhibiting apoptosis through phosphorylation and inactivation of several targets, including Bad, forkhead transcription factors, c-Raf and caspase-9. In addition to its role in survival and glycogen synthesis, Akt is involved in cell cycle regulation. Akt also plays a critical role in cell growth by directly phosphorylating mTOR in a rapamycin-sensitive complex containing raptor. Mutation of the glutamic acid at residue 17 to lysine (E17K) of Akt was initially identified in human breast, colorectal and ovarian cancers. This conserved glutamic acid residue is located at the lipid-binding pocket of the Akt plextrin homology domain. The E17K mutation increases the affinity between Akt and phospholipids at the plasma membrane, leading to increased Akt recruitment, super-activation of the Akt pathway, cellular transformation and tumor formation. Additional studies detect the presence of the Akt (E17K) mutation in multiple cancers, including lung cancer, prostate cancer, endometrial carcinoma and several melanomas.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161







![Akt1 antibody immunoprecipitates Akt1 protein in IP experiments. IP samples: 30 μg whole cell extract of Akt1-transfected 293T cells. A. 30 μg whole cell extract of Akt1-protein expressing 293T cell B. Control with 3 μg of preimmune Rabbit IgG C. Immunoprecipitation of Akt1 protein by 3 μg Akt1 antibody (GTX110613) 10 % SDS-PAGE The immunoprecipitated Akt1 protein was detected by Akt1 antibody (GTX110613) diluted at 1:5000. [EasyBlot anti-rabbit IgG (GTX221666-01) was used as a secondary reagent]](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX110613/GTX110613_40051_IP_w_23060500_283.webp)