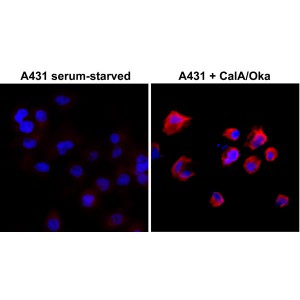
Immunocytochemistry of serum-starved A431 cells nontreated or treated with Calyculin A/ Okadaic Acid, using RevMAb Clone RM102 at 1/500 dilution (followed by PE conjugated secondary antibody, red) and DAPI (blue).
anti-Phosphothreonine, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM102)
REV-31-1009-00
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityAll Species
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Phosphothreonine, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM102)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM102
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to threonine-phosphorylated proteins. No cross reactivity with nonphosphorylated threonine, phosphoserine, and phosphotyrosine. It shows slight cross-reactivity with a few phospho-serine-containing peptides. Applications: WB, IP, ICC, IHC, FACS, ELISA. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Threonine is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications (PTMs). The hydroxyl side-chain can undergo O-linked glycosylation. In addition, threonine residues undergo phosphorylation through the action of a threonine kinase. In its phosphorylated form, it can be referred to as phosphothreonine. Phosphothreonine has three potential coordination sites (carboxyl, amine and phosphate group) and determination of the mode of coordination between phosphorylated ligands and metal ions occurring in an organism is important to explain the function of the phosphothreonine in biological processes. - Threonine is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications (PTMs). The hydroxyl side-chain can undergo O-linked glycosylation. In addition, threonine residues undergo phosphorylation through the action of a threonine kinase. In its phosphorylated form, it can be referred to as phosphothreonine. Phosphothreonine has three potential coordination sites (carboxyl, amine and phosphate group) and determination of the mode of coordination between phosphorylated ligands and metal ions occurring in an organism is important to explain the function of the phosphothreonine in biological processes.
- ReactivityAll Species
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
