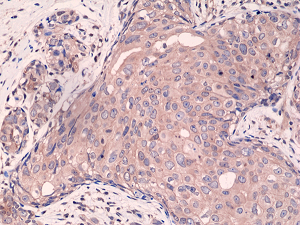
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue sections using Anti-Smad4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM277) at a 1:2000 dilution.
anti-Smad4 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM277)
REV-31-1158-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSMAD4
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Smad4 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM277)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM277
- Gene ID4089
- Target nameSMAD4
- Target descriptionSMAD family member 4
- Target synonymsDPC4, JIP, MADH4, MYHRS, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4, MAD homolog 4, SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 4, deleted in pancreatic carcinoma locus 4, deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4, mothers against decapentaplegic, Drosophila, homolog of, 4
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ13485
- Protein NameMothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4
- Scientific DescriptionMembers of the Smad family of signal transduction molecules are components of a critical intracellular pathway that transmits TGF-beta signals from the cell surface into the nucleus. Three distinct classes of Smads have been defined: the receptor-regulated Smads (R-Smads), which include Smad1, 2, 3, 5, 8; the common-mediator Smad (co-Smad), Smad4; and the antagonistic or inhibitory Smads (I-Smads), Smad6 and 7. Binding of the TGF-beta superfamily of ligands that includes Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-beta) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) to its cognate receptor allows phosphorylation of Smad 1, 2, 3, 5 and 8 (R-Smad, Receptor Smad). This signals for heterotrimerization with Smad4 (co-Smad, co-mediator Smad) and translocation of the complex to the nucleus. Inhibitory or antagonistic Smad (I-Smad) that includes Smad 6 and 7, interact with activated R-Smads and attenuate the signaling pathway. Smad4 acts as a tumor suppressor protein by transcriptionally regulating its target genes such as Cyclin D1 (downregulation) and collagen (upregulation) that inhibit cell proliferation. Dephosphorylation regulates nuclear export and nucleocytoplasmic dynamics of Smads. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Smad4. This antibody may also react to mouse or rat Smad4, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Members of the Smad family of signal transduction molecules are components of a critical intracellular pathway that transmits TGF-beta signals from the cell surface into the nucleus. Three distinct classes of Smads have been defined: the receptor-regulated Smads (R-Smads), which include Smad1, 2, 3, 5, 8; the common-mediator Smad (co-Smad), Smad4; and the antagonistic or inhibitory Smads (I-Smads), Smad6 and 7. Binding of the TGF-beta superfamily of ligands that includes Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-beta) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) to its cognate receptor allows phosphorylation of Smad 1, 2, 3, 5 and 8 (R-Smad, Receptor Smad). This signals for heterotrimerization with Smad4 (co-Smad, co-mediator Smad) and translocation of the complex to the nucleus. Inhibitory or antagonistic Smad (I-Smad) that includes Smad 6 and 7, interact with activated R-Smads and attenuate the signaling pathway. Smad4 acts as a tumor suppressor protein by transcriptionally regulating its target genes such as Cyclin D1 (downregulation) and collagen (upregulation) that inhibit cell proliferation. Dephosphorylation regulates nuclear export and nucleocytoplasmic dynamics of Smads.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161




