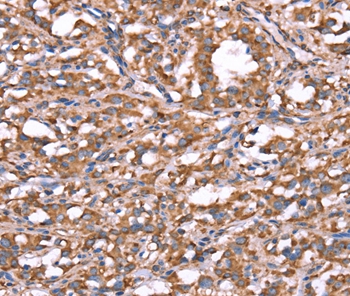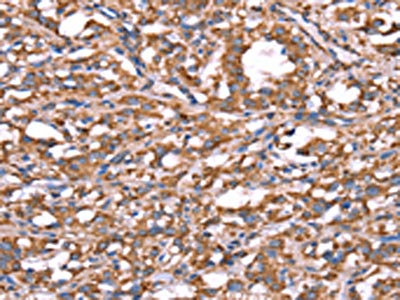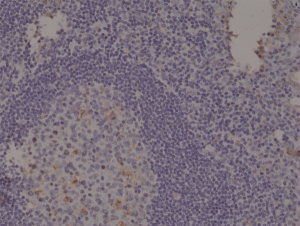
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human Tonsil tissue section using anti-Spastin rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM346) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-Spastin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM346)
REV-31-1232-00
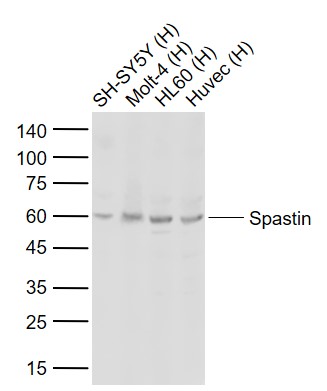
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSPAST
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Spastin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM346)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM346
- Gene ID6683
- Target nameSPAST
- Target descriptionspastin
- Target synonymsADPSP, FSP2, SPG4, spastin, spastic paraplegia 4 (autosomal dominant; spastin), spastic paraplegia 4 protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UBP0
- Protein NameSpastin
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Spastin. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Spastin is a microtubule-severing protein that cleaves longer microtubules (MTs) to shorter ones. The severing of MT regulates its numbers and mobility, and the distribution of the plus-end. This has also been related to membrane trafficking of microtubules. Mutations in the spastin gene SPG4 is the main cause for hereditary spastic paraplegia, a neurodegenerative disorder mainly occurring in corticospinal tracks. - Spastin is a microtubule-severing protein that cleaves longer microtubules (MTs) to shorter ones. The severing of MT regulates its numbers and mobility, and the distribution of the plus-end. This has also been related to membrane trafficking of microtubules. Mutations in the spastin gene SPG4 is the main cause for hereditary spastic paraplegia, a neurodegenerative disorder mainly occurring in corticospinal tracks.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161