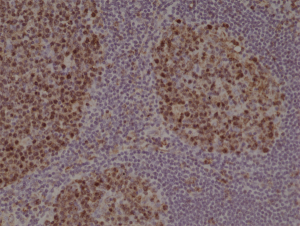
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human Tonsil tissue section using anti-Stathmin rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM350) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-Stathmin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM350)
REV-31-1236-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSTMN1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Stathmin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM350)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM350
- Gene ID3925
- Target nameSTMN1
- Target descriptionstathmin 1
- Target synonymsC1orf215, LAP18, Lag, OP18, PP17, PP19, PR22, SMN, stathmin, leukemia-associated phosphoprotein p18, metablastin, oncoprotein 18, phosphoprotein 19, phosphoprotein p19, prosolin, stathmin 1/oncoprotein 18, testicular tissue protein Li 189, transmembrane protein C1orf215
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP16949
- Protein NameStathmin
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Stathmin. It may also react to mouse or rat Stathmin, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Stathmin belongs to the stathmin family of genes. It encodes a ubiquitous cytosolic phosphoprotein proposed to function as an intracellular relay integrating regulatory signals of the cellular environment. Stathmin regulates microtubule dynamics by promoting depolymerization of microtubules and/or preventing polymerization of tubulin heterodimers. Upon entry into mitosis, microtubules polymerize to form the mitotic spindle, a cellular structure that is essential for accurate chromosome segregation and cell division. The microtubule-depolymerizing activity of stathmin is switched off at the onset of mitosis by phosphorylation to allow microtubule polymerization and assembly of the mitotic spindle. Phosphorylated stathmin has to be reactivated by dephosphorylation before cells exit mitosis and enter a new interphase. Stathmin is critically important for the formation of a normal mitotic spindle upon entry into mitosis and also for the regulation of the function of the mitotic spindle in the later stages of mitosis and for the timely exit from mitosis. - Stathmin belongs to the stathmin family of genes. It encodes a ubiquitous cytosolic phosphoprotein proposed to function as an intracellular relay integrating regulatory signals of the cellular environment. Stathmin regulates microtubule dynamics by promoting depolymerization of microtubules and/or preventing polymerization of tubulin heterodimers. Upon entry into mitosis, microtubules polymerize to form the mitotic spindle, a cellular structure that is essential for accurate chromosome segregation and cell division. The microtubule-depolymerizing activity of stathmin is switched off at the onset of mitosis by phosphorylation to allow microtubule polymerization and assembly of the mitotic spindle. Phosphorylated stathmin has to be reactivated by dephosphorylation before cells exit mitosis and enter a new interphase. Stathmin is critically important for the formation of a normal mitotic spindle upon entry into mitosis and also for the regulation of the function of the mitotic spindle in the later stages of mitosis and for the timely exit from mitosis.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161







![Stathmin 1 antibody detects Stathmin 1 protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: SK-N-SH cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Stathmin 1 protein stained by Stathmin 1 antibody (GTX104707) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX104707/GTX104707_39694_20150410_IFA_2_w_23060120_858.webp)