anti-VASP (human), pAb
AG-25T-0112
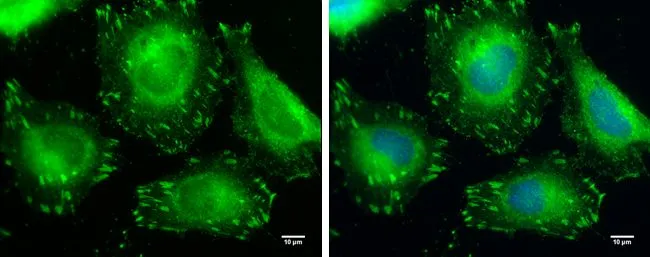
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetVASP
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-VASP (human), pAb
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Gene ID7408
- Target nameVASP
- Target descriptionvasodilator stimulated phosphoprotein
- Target synonymsvasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein
- HostRabbit
- Protein IDP50552
- Protein NameVasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein
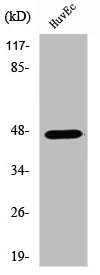
- Scientific DescriptionPolyclonal Antibody. Recognizes both the 46kDa (Ser157 dephospho-) and 50kDa (Ser157 phospho-) form of human VASP. Does not cross-react with mouse or rat VASP. Source: Rabbit. Applications: ICC, IP, WB. Liquid. Crude serum containing 0.02% sodium azide. VASP (vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein) is a proline-rich protein substrate of cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases. VASP is an actin-associated protein involved in a range of processes dependent on cytoskeleton remodeling and cell polarity such as axon guidance, lamellipodial and filopodial dynamics, platelet activation and cell migration. VASP promotes actin filament elongation. It protects the barbed end of growing actin filaments against capping and increases the rate of actin polymerization in the presence of capping proteins. VASP stimulates actin filament elongation by promoting the transfer of profilin-bound actin monomers onto the barbed end of growing actin filaments and it plays a role in actin-based mobility of Listeria monocytogenes in host cells. It regulates actin dynamics in platelets and plays an important role in regulating platelet aggregation. VASP phosphorylation is used to monitor the effect of so-called antiplatelet drugs that reduce platelet reactivity and are used to prevent stent thrombosis, strokes and heart attacks in patients. Phosphorylation of VASP at Ser157 causes a mobility shift in SDS gel electrophoresis from 46 to 50kDa, which has been used as a convenient marker to monitor cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinase activity. - VASP (vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein) is a proline-rich protein substrate of cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases. VASP is an actin-associated protein involved in a range of processes dependent on cytoskeleton remodeling and cell polarity such as axon guidance, lamellipodial and filopodial dynamics, platelet activation and cell migration. VASP promotes actin filament elongation. It protects the barbed end of growing actin filaments against capping and increases the rate of actin polymerization in the presence of capping proteins. VASP stimulates actin filament elongation by promoting the transfer of profilin-bound actin monomers onto the barbed end of growing actin filaments and it plays a role in actin-based mobility of Listeria monocytogenes in host cells. It regulates actin dynamics in platelets and plays an important role in regulating platelet aggregation. VASP phosphorylation is used to monitor the effect of so-called antiplatelet drugs that reduce platelet reactivity and are used to prevent stent thrombosis, strokes and heart attacks in patients. Phosphorylation of VASP at Ser157 causes a mobility shift in SDS gel electrophoresis from 46 to 50kDa, which has been used as a convenient marker to monitor cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinase activity.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161