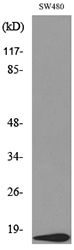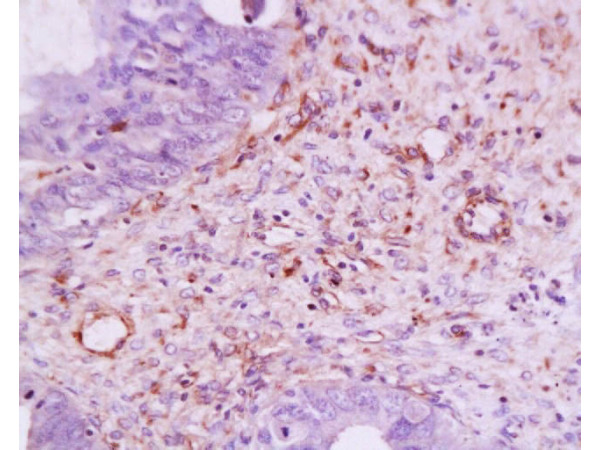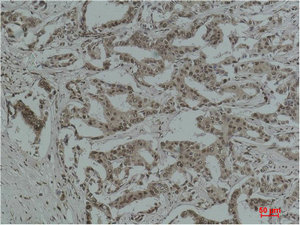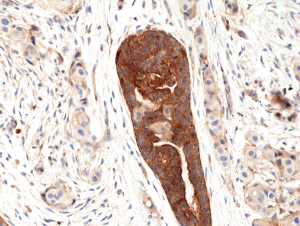
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue section using anti-VEGF rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM391) at a 1:100 dilution.
anti-VEGFA (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM391)
REV-31-1277-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetVEGFA
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-VEGFA (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM391)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM391
- Gene ID7422
- Target nameVEGFA
- Target descriptionvascular endothelial growth factor A
- Target synonymsL-VEGF, MVCD1, VEGF, VPF, vascular endothelial growth factor A, long form, vascular endothelial growth factor A121, vascular endothelial growth factor A165, vascular permeability factor
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP15692
- Protein NameVascular endothelial growth factor A, long form
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human VEGFA. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) is a 45 kDa homodimeric disulfide-linked glycoprotein involved in angiogenesis which promotes tumor progression and metastasis. VEGF has a variety of effects on vascular endothelium, including the ability to promote endothelial cell viability, mitogenesis, chemotaxis and vascular permeability. The VEGF family currently includes VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, VEGF-E and PIGF. VEGF and its receptor system have been shown to be the fundamental regulators in the cell signaling of angiogenesis. Most tumors have the absolute requirement of angiogenesis, and VEGF has been described as the most potent angiogenic cytokine linked to this process. VEGF-A binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. VEGF-A is a specific mitogen for vascular endothelial cells and a strong angiogenic factor in vivo. In addition to its action as a mitogen it is a potent vascular permeability factor (VPF) in vivo. It is also a chemoattractant molecule for monocytes and endothelial cells. It induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels. - VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) is a 45 kDa homodimeric disulfide-linked glycoprotein involved in angiogenesis which promotes tumor progression and metastasis. VEGF has a variety of effects on vascular endothelium, including the ability to promote endothelial cell viability, mitogenesis, chemotaxis and vascular permeability. The VEGF family currently includes VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, VEGF-E and PIGF. VEGF and its receptor system have been shown to be the fundamental regulators in the cell signaling of angiogenesis. Most tumors have the absolute requirement of angiogenesis, and VEGF has been described as the most potent angiogenic cytokine linked to this process. VEGF-A binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. VEGF-A is a specific mitogen for vascular endothelial cells and a strong angiogenic factor in vivo. In addition to its action as a mitogen it is a potent vascular permeability factor (VPF) in vivo. It is also a chemoattractant molecule for monocytes and endothelial cells. It induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161