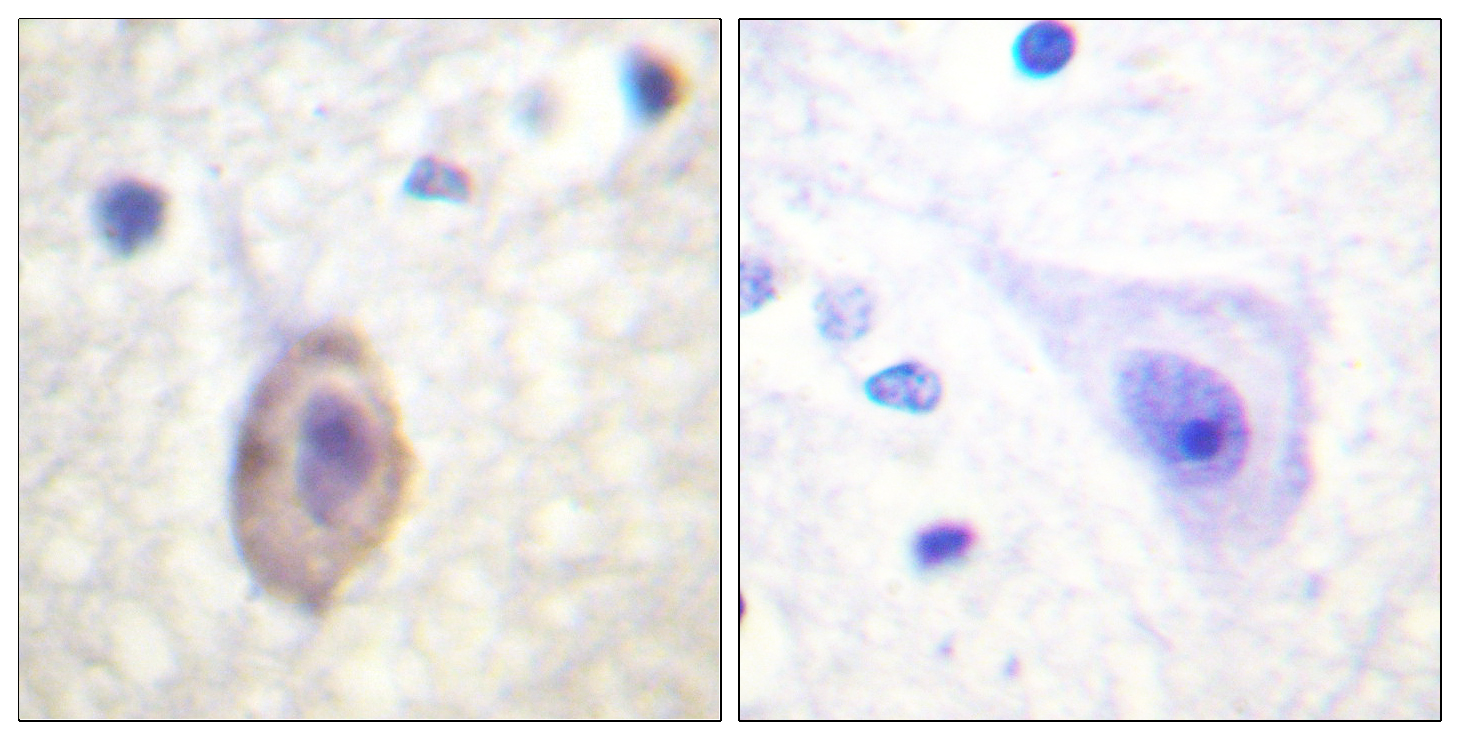
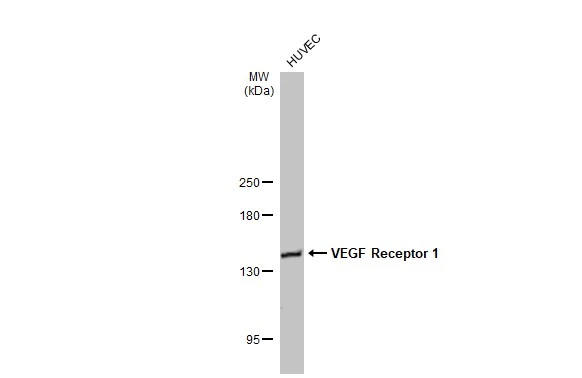
anti-VEGFR-1 (human), mAb (EWC)
AG-20T-0106
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetFLT1
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-VEGFR-1 (human), mAb (EWC)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDEWC
- Gene ID2321
- Target nameFLT1
- Target descriptionfms related receptor tyrosine kinase 1
- Target synonymsFLT, FLT-1, VEGFR-1, VEGFR1, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1, fms related tyrosine kinase 1, fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 (vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor receptor), tyrosine-protein kinase FRT, tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT, vascular permeability factor receptor
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP17948
- Protein NameVascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1
- Scientific DescriptionMonoclonal Antibody. The antibody will detect native human VEGFR-1/Flt-1 in ELISA experiments and on the surface of different human cell types. Isotype: Mouse IgG1. Clone: EWC. Applications: ELISA, WB. Lyophilized. Recombinant human soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1) is the naturally occurring form and is a glycosylated monomeric protein. The biological function of sVEGFR-1 seems to be an endogenous regulator of angiogenesis, binding VEGF with the same affinity as the full-length receptor. VEGFR-1 is a tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB and PGF, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis and cancer cell invasion. It may play an essential role as a negative regulator of embryonic angiogenesis by inhibiting excessive proliferation of endothelial cells. It can promote endothelial cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis in adulthood. Its function in promoting cell proliferation seems to be cell-type specific. Promotes PGF-mediated proliferation of endothelial cells, proliferation of some types of cancer cells, but does not promote proliferation of normal fibroblasts (in vitro). It has a very high affinity for VEGFA and relatively low protein kinase activity. It may function as a negative regulator of VEGFA signaling by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and preventing its binding to KDR. Modulates KDR signaling by forming heterodimers with KDR. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of phospholipase C-gamma (PLCG) leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leading to activation of phosphatidylinositol kinase and the downstream signaling pathway. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Phosphorylates SRC and YES1 and may also phosphorylate CBL. - Recombinant human soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1) is the naturally occurring form and is a glycosylated monomeric protein. The biological function of sVEGFR-1 seems to be an endogenous regulator of angiogenesis, binding VEGF with the same affinity as the full-length receptor. VEGFR-1 is a tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB and PGF, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis and cancer cell invasion. It may play an essential role as a negative regulator of embryonic angiogenesis by inhibiting excessive proliferation of endothelial cells. It can promote endothelial cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis in adulthood. Its function in promoting cell proliferation seems to be cell-type specific. Promotes PGF-mediated proliferation of endothelial cells, proliferation of some types of cancer cells, but does not promote proliferation of normal fibroblasts (in vitro). It has a very high affinity for VEGFA and relatively low protein kinase activity. It may function as a negative regulator of VEGFA signaling by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and preventing its binding to KDR. Modulates KDR signaling by forming heterodimers with KDR. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of phospholipase C-gamma (PLCG) leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leading to activation of phosphatidylinositol kinase and the downstream signaling pathway. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Phosphorylates SRC and YES1 and may also phosphorylate CBL.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161