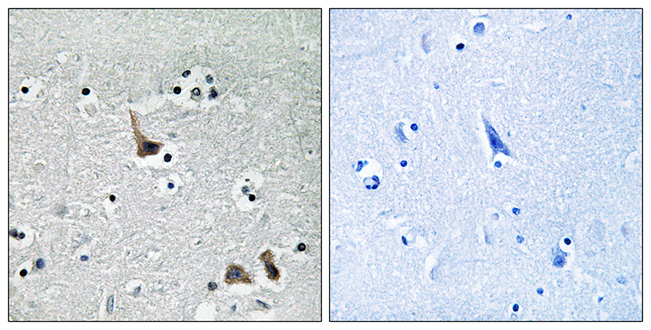
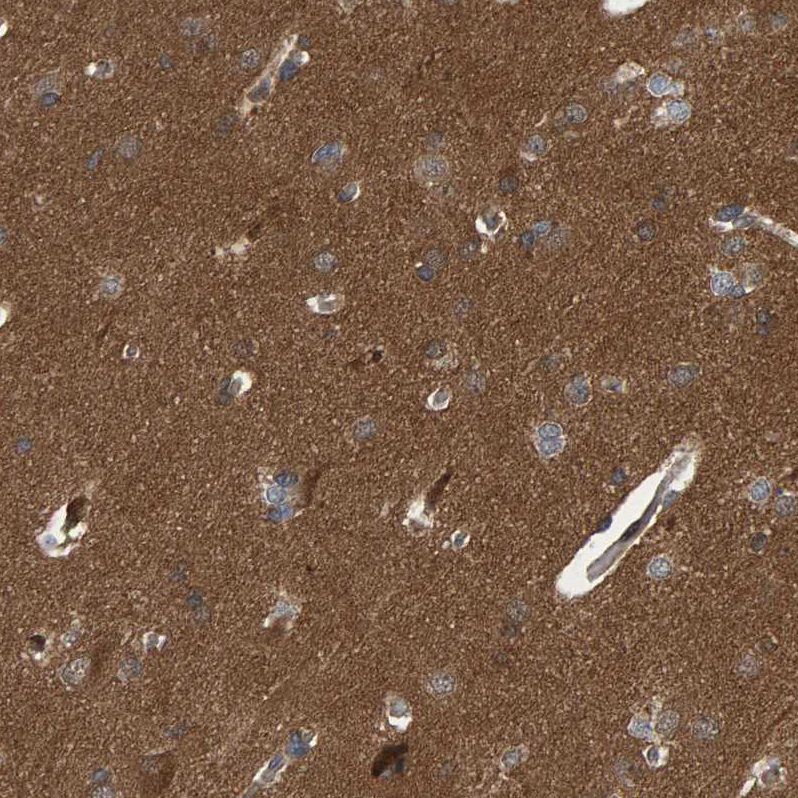
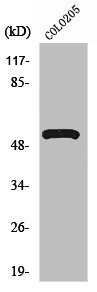
ATP6V1H antibody [N3C3]
GTX110778
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat, Zebra Fish
TargetATP6V1H
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameATP6V1H antibody [N3C3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.76 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID51606
- Target nameATP6V1H
- Target descriptionATPase H+ transporting V1 subunit H
- Target synonymsCGI-11, MSTP042, NBP1, SFD, SFDalpha, SFDbeta, VMA13, V-type proton ATPase subunit H, ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 50/57kDa, V1 subunit H, V-ATPase 50/57 kDa subunits, V-ATPase subunit H, nef-binding protein 1, protein VMA13 homolog, vacuolar ATP synthase subunit H, vacuolar ATPase subunit H, vacuolar proton pump subunit H, vacuolar proton pump subunit SFD
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UI12
- Protein NameV-type proton ATPase subunit H
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c, c, and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This gene encodes the regulatory H subunit of the V1 domain which is required for catalysis of ATP but not the assembly of V-ATPase. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encode two isoforms of the H subunit. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat, Zebra Fish
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Choy CH, Saffi G, Gray MA, et al. Lysosome enlargement during inhibition of the lipid kinase PIKfyve proceeds through lysosome coalescence. J Cell Sci. 2018,131(10). doi: 10.1242/jcs.213587Read this paper
- Gondim MV, Wiltzer-Bach L, Maurer B, et al. AP-2 Is the Crucial Clathrin Adaptor Protein for CD4 Downmodulation by HIV-1 Nef in Infected Primary CD4+ T Cells. J Virol. 2015,89(24):12518-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01838-15Read this paper