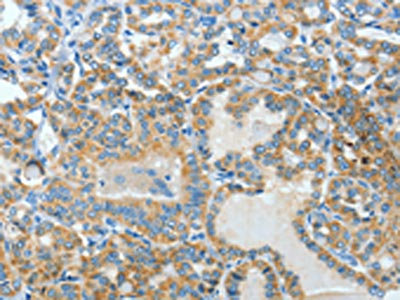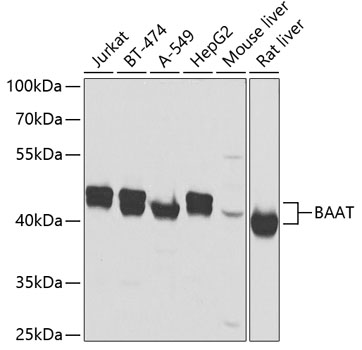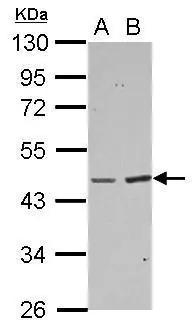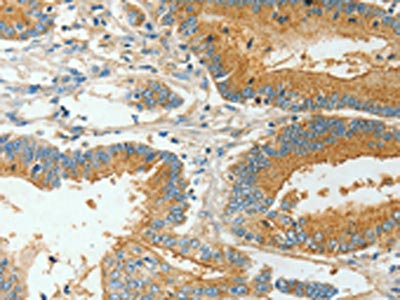
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human colon cancer tissue using CSB-PA194965(BAAT Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200)
BAAT Antibody
CSB-PA194965
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetBAAT
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameBAAT Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID570
- Target nameBAAT
- Target descriptionbile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase
- Target synonymsBACAT, BACD1, BAT, FHCA3, HCHO, bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase, bile acid CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase (glycine N-choloyltransferase), bile acid Coenzyme A: amino acid N-acyltransferase (glycine N-choloyltransferase), bile acid-CoA thioesterase, choloyl-CoA hydrolase, long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA hydrolase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ14032
- Protein NameBile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a liver enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of C24 bile acids from the acyl-CoA thioester to either glycine or taurine, the second step in the formation of bile acid-amino acid conjugates. The bile acid conjugates then act as a detergent in the gastrointestinal tract, which enhances lipid and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. Defects in this gene are a cause of familial hypercholanemia (FHCA). Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161