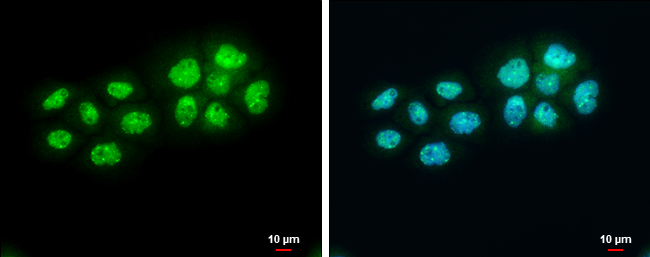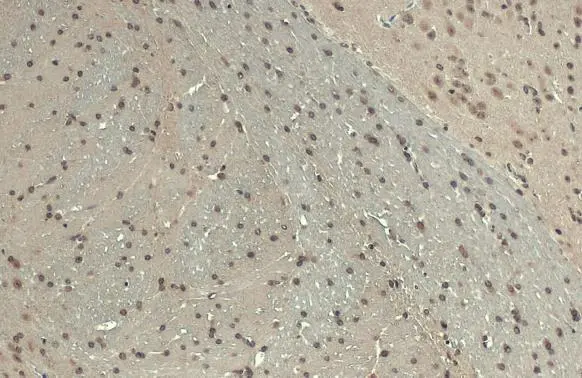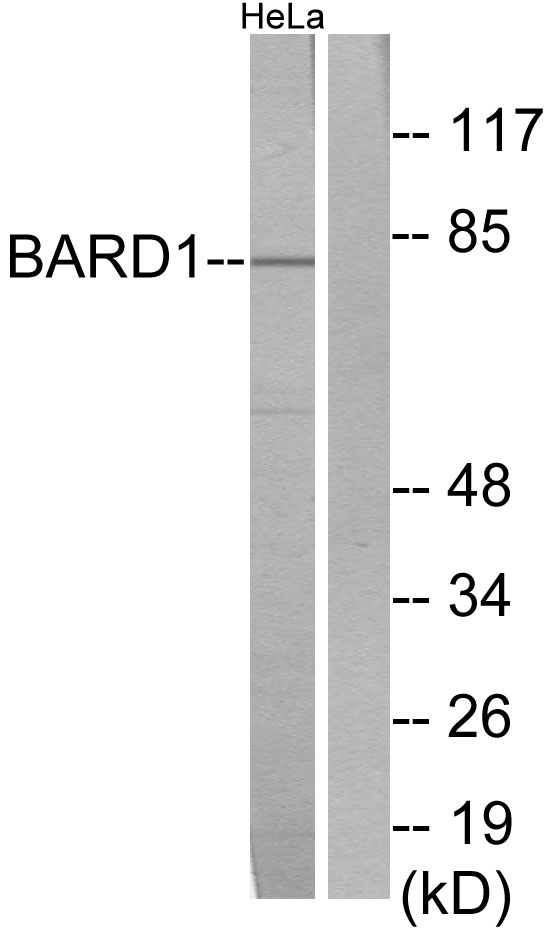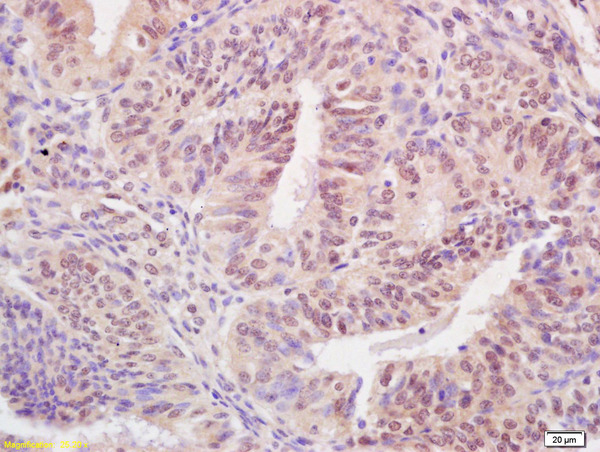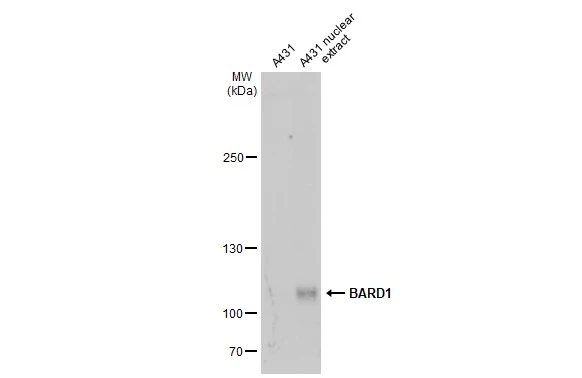
A431 whole cell and nuclear extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with BARD1 antibody (GTX132094) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
BARD1 antibody
GTX132094
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetBARD1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameBARD1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.58 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID580
- Target nameBARD1
- Target descriptionBRCA1 associated RING domain 1
- Target synonymsBRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1, BRCA1-associated RING domain gene 1, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase BARD1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ99728
- Protein NameBRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a protein which interacts with the N-terminal region of BRCA1. In addition to its ability to bind BRCA1 in vivo and in vitro, it shares homology with the 2 most conserved regions of BRCA1: the N-terminal RING motif and the C-terminal BRCT domain. The RING motif is a cysteine-rich sequence found in a variety of proteins that regulate cell growth, including the products of tumor suppressor genes and dominant protooncogenes. This protein also contains 3 tandem ankyrin repeats. The BARD1/BRCA1 interaction is disrupted by tumorigenic amino acid substitutions in BRCA1, implying that the formation of a stable complex between these proteins may be an essential aspect of BRCA1 tumor suppression. This protein may be the target of oncogenic mutations in breast or ovarian cancer. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161