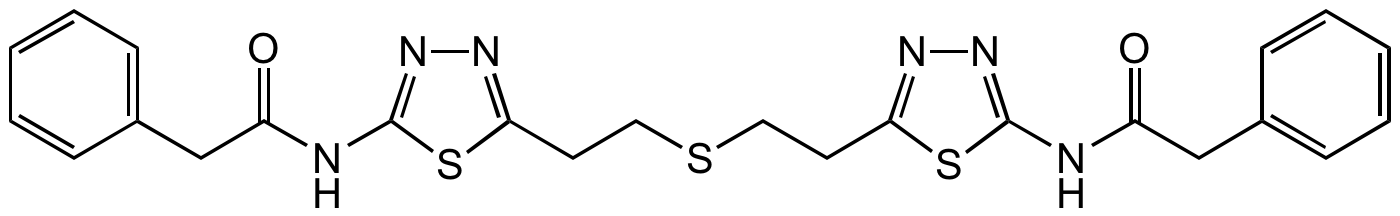
Chemical Structure
BPTES [314045-39-1]
AG-CR1-3690
CAS Number314045-39-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight524.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameBPTES [314045-39-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number314045-39-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC24H24N6O2S3
- Molecular Weight524.7
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 314045-39-1. Formula: C24H24N6O2S3. MW: 524.7. . Selective, allosteric non-competitive inhibitor of glutaminase 1 (GLS1), selective for GLS1 over GLS2, glutamate dehydrogenase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, consequently inhibiting glutaminolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Glutaminase converts glutamine to glutamate, which is an important excitatory neurotransmitter in brain and can be further oxidized to alpha-ketoglutarate to feed the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and to glutathione, which is important for controlling the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), particularly important for cancer cell growth. Anticancer agent. Increases the production of reactive oxygen species and reduces ATP levels in hypoxic cells, induces cell death of P493 human lymphoma B cells in vitro and delays tumor xenograft growth in vivo. - Selective, allosteric non-competitive inhibitor of glutaminase 1 (GLS1), selective for GLS1 over GLS2, glutamate dehydrogenase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, consequently inhibiting glutaminolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Glutaminase converts glutamine to glutamate, which is an important excitatory neurotransmitter in brain and can be further oxidized to alpha-ketoglutarate to feed the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and to glutathione, which is important for controlling the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), particularly important for cancer cell growth. Anticancer agent. Increases the production of reactive oxygen species and reduces ATP levels in hypoxic cells, induces cell death of P493 human lymphoma B cells in vitro and delays tumor xenograft growth in vivo.
- SMILESO=C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC2=NN=C(CCSCCC3=NN=C(NC(CC4=CC=CC=C4)=O)S3)S2
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![BPTES [314045-39-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/6D/CgoaEWayH2eEYBZ6AAAAAMWDh2o324.png)