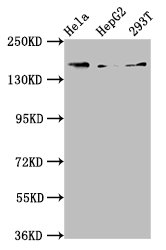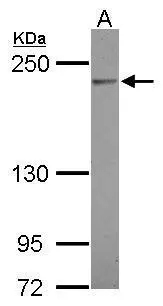
Sample (30 ug of whole cell lysate) A: HepG2 5% SDS PAGE GTX110413 diluted at 1:500
C4 / C4b antibody [N1N2-2], N-term
GTX110413
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetC4A
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameC4 / C4b antibody [N1N2-2], N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.52 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID720
- Target nameC4A
- Target descriptioncomplement C4A (Chido/Rodgers blood group)
- Target synonymsC4, C4A2, C4A3, C4A4, C4A6, C4AD, C4S, CO4, CPAMD2, RG, complement C4-A, C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain-containing protein 2, C4A anaphylatoxin, MHC class III region complement, Rodgers form of C4, acidic C4, acidic complement C4, complement C4A (Rodgers blood group), complement component 4A (Rodgers blood group)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the acidic form of complement factor 4, part of the classical activation pathway. The protein is expressed as a single chain precursor which is proteolytically cleaved into a trimer of alpha, beta, and gamma chains prior to secretion. The trimer provides a surface for interaction between the antigen-antibody complex and other complement components. The alpha chain may be cleaved to release C4 anaphylatoxin, a mediator of local inflammation. Deficiency of this protein is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus and type I diabetes mellitus. This gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. Varying haplotypes of this gene cluster exist, such that individuals may have 1, 2, or 3 copies of this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human hepatoma, using C4 antibody [N1N2-2], N-term(GTX110413) antibody at 1:200 dilution.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human hepatoma, using C4 antibody [N1N2-2], N-term(GTX110413) antibody at 1:200 dilution.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX110413/GTX110413_40478_IHC_w_23060500_405.webp)