Chemical Structure
C646 [328968-36-1] [328968-36-1]
AG-CR1-3508
CAS Number328968-36-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight445.4
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameC646 [328968-36-1] [328968-36-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number328968-36-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
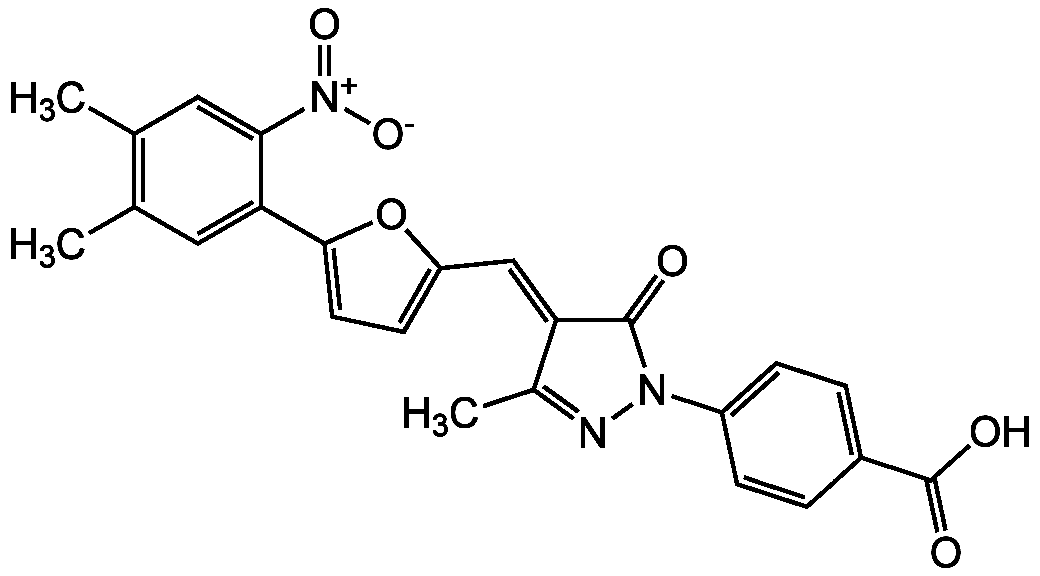
- Molecular FormulaC24H19N3O6
- Molecular Weight445.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 328968-36-1. Formula: C24H19N3O6. MW: 445.4. Reversible cell permeable p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase (HAT) inhibitor. Specific inhibition to p300 (86%) compared to N-acetyltransferase, PCAF, GCN5, Rtt109, Sas or MOZ histone acetyltransferases (<10%). Cell growth inhibitor in melanoma and non-small-cell-lung (NSCL) human cancer cell lines. - Reversible cell permeable p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase (HAT) inhibitor. Specific inhibition to p300 (86%) compared to N-acetyltransferase, PCAF, GCN5, Rtt109, Sas or MOZ histone acetyltransferases (<10%). Cell growth inhibitor in melanoma and non-small-cell-lung (NSCL) human cancer cell lines.
- SMILESCC1=NN(C(=O)\C1=C\C1=CC=C(O1)C1=CC(C)=C(C)C=C1[N+]([O-])=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200



![C646 [328968-36-1]](https://bpsbioscience.com/media/catalog/product/c/6/c646.png)

![C646 [328968-36-1] [328968-36-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/67/CgoaEWayHsWEHmNAAAAAAGIbeK4152.png)