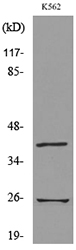
CD161 antibody [HP-3G10]
GTX01454
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Primate
TargetKLRB1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD161 antibody [HP-3G10]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier Note*Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDHP-3G10
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3820
- Target nameKLRB1
- Target descriptionkiller cell lectin like receptor B1
- Target synonymsCD161, CLEC5B, NKR, NKR-P1, NKR-P1A, NKRP1A, hNKR-P1A, killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1, C-type lectin domain family 5 member B, killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B, member 1, natural killer cell surface protein P1A
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDQ12918
- Protein NameKiller cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1
- Scientific DescriptionNatural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that mediate cytotoxicity and secrete cytokines after immune stimulation. Several genes of the C-type lectin superfamily, including the rodent NKRP1 family of glycoproteins, are expressed by NK cells and may be involved in the regulation of NK cell function. The KLRB1 protein contains an extracellular domain with several motifs characteristic of C-type lectins, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. The KLRB1 protein is classified as a type II membrane protein because it has an external C terminus. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Primate
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161