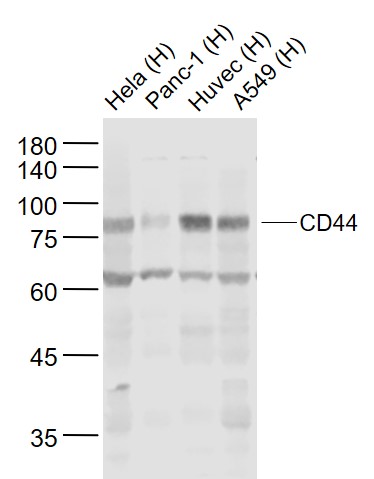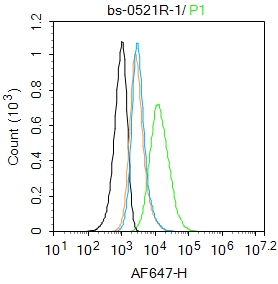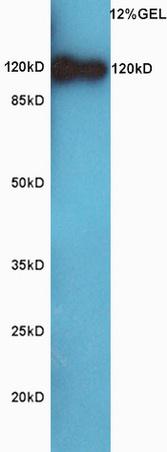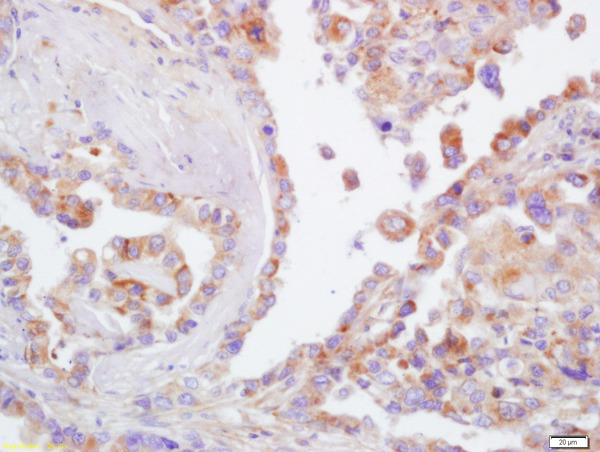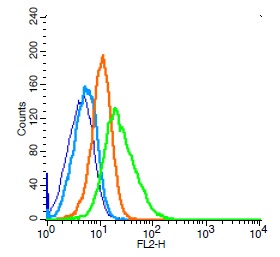
Human Raji cells probed with CD44 Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (bs-0521R) (green) at 1:100 for 30 minutes followed by a PE conjugated secondary antibody compared to unstained cells (blue), secondary only (light blue), and isotype control (orange).
CD44 Polyclonal Antibody
BS-0521R
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Canine, Equine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rabbit, Rat
TargetCD44
Overview
- SupplierBioss
- Product NameCD44 Polyclonal Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer16
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- Applications SupplierWB(1:300-5000), ELISA(1:500-1000), FCM(1:20-100), IHC-P(1:200-400), IF(IHC-P)(1:50-200), IF(ICC)(1:50-200)
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 ug/ul
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID960
- Target nameCD44
- Target descriptionCD44 molecule (IN blood group)
- Target synonymsCDW44, CSPG8, ECM-III, ECMR-III, H-CAM, HCELL, HUTCH-1, HUTCH-I, Hermes-1, LHR, MC56, MDU2, MDU3, MIC4, Pgp1, CD44 antigen, CD44 molecule (Indian blood group), GP90 lymphocyte homing/adhesion receptor, Hermes antigen, In(Lu) related-p80, Indian blood group antigen, cell surface glycoprotein CD44, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 8, epican, extracellular matrix receptor III, hematopoietic cell E- and L-selectin ligand, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, homing cell adhesion molecule, homing function and Indian blood group system, hyaluronate receptor, phagocyte glycoprotein 1, phagocytic glycoprotein 1, soluble CD44
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP16070
- Protein NameCD44 antigen
- ReactivityBovine, Canine, Equine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rabbit, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- The biological characteristics of sheep umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Chen F et al., 2018 Jul, Can J Vet ResRead this paper
- The glycoprotein GPNMB attenuates astrocyte inflammatory responses through the CD44 receptor. Neal ML et al., 2018 Mar 8, J NeuroinflammationRead this paper
- Bone mesenchymal stem cells co-expressing VEGF and BMP-6 genes to combat avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Liao H et al., 2018 Jan, Exp Ther MedRead this paper
- Effects of neuritin on the differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into neuron-like cells. Zhu J et al., 2017 Sep, Mol Med RepRead this paper
- Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem-Cell Transplantation Promotes Functional Improvement Associated with CNTF-STAT3 Activation after Hemi-Sectioned Spinal Cord Injury in Tree Shrews. Xiong LL et al., 2017, Front Cell NeurosciRead this paper
- NIBP impacts on the expression of E-cadherin, CD44 and vimentin in colon cancer via the NF-kappaB pathway. Xu CY et al., 2016 Jun, Mol Med RepRead this paper
- Subchondral bone changes and chondrogenic capacity of progenitor cells from subchondral bone in the collagenase-induced temporomandibular joints osteoarthritis rabbit model. Wu G et al., 2015, Int J Clin Exp PatholRead this paper
- Characterization of sphere-forming cells with stem-like properties from the gastric cancer cell lines MKN45 and SGC7901. Wang X et al., 2014 Dec, Mol Med RepRead this paper