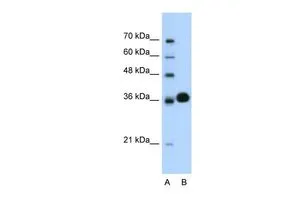
![Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_44580_20230414_WB_M_23041723_378.webp)
Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
CDK6 antibody [N1C3]
GTX103992
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCDK6
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCDK6 antibody [N1C3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.14 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1021
- Target nameCDK6
- Target descriptioncyclin dependent kinase 6
- Target synonymsMCPH12, PLSTIRE, cyclin-dependent kinase 6, cell division protein kinase 6, serine/threonine-protein kinase PLSTIRE
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ00534
- Protein NameCyclin-dependent kinase 6
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase (CDK) family. CDK family members are highly similar to the gene products of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc28, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc2, and are known to be important regulators of cell cycle progression. This kinase is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression and G1/S transition. The activity of this kinase first appears in mid-G1 phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits including D-type cyclins and members of INK4 family of CDK inhibitors. This kinase, as well as CDK4, has been shown to phosphorylate, and thus regulate the activity of, tumor suppressor protein Rb. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_44580_20230414_WB_R_23041723_127.webp)
![CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus on human colon carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma. CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus on human colon carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma. CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_40135_20141219_IHC_w_23060120_899.webp)
![CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus in human lung adenocarcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human lung adenocarcinoma. CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus in human lung adenocarcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human lung adenocarcinoma. CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_40135_20151227_IHC-P_w_23060120_361.webp)
![CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse thymus gland. CDK6 stained by CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:1000. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse thymus gland. CDK6 stained by CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:1000. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_43810_20200401_IHC-P_M_w_23060120_776.webp)
![CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: CDK6 stained by CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Scale bar= 10μm. CDK6 antibody [N1C3] detects CDK6 protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: CDK6 stained by CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Scale bar= 10μm.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_44545_20220401_ICC_IF_w_23060120_727.webp)
![Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_45008_20230414_WB_R_24070301_395.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [N1C3] (GTX103992) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX103992/GTX103992_45008_20230414_WB_24070301_287.webp)
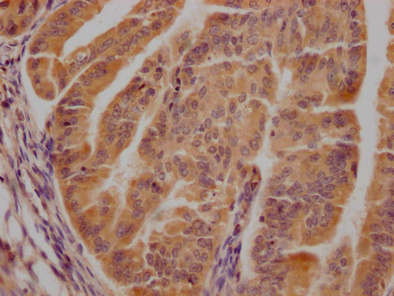



![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extract (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with CDK6 antibody [HL2078] (GTX637986) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX637986/GTX637986_T-44893_20230707_WB_multiple_B_23071223_517.webp)
![WB analysis of MOLT4 cell lysate using GTX75692 CDK6 antibody [DCS 83.1].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX75692/GTX75692_3236_WB_w_23051501_440.webp)