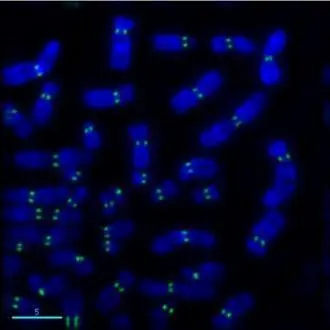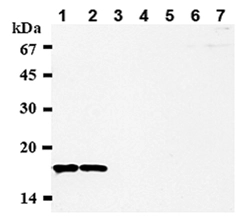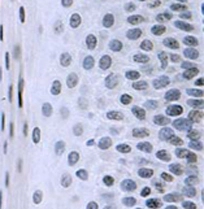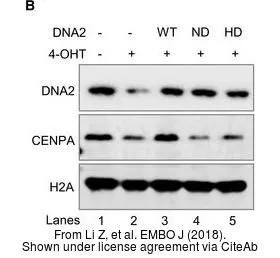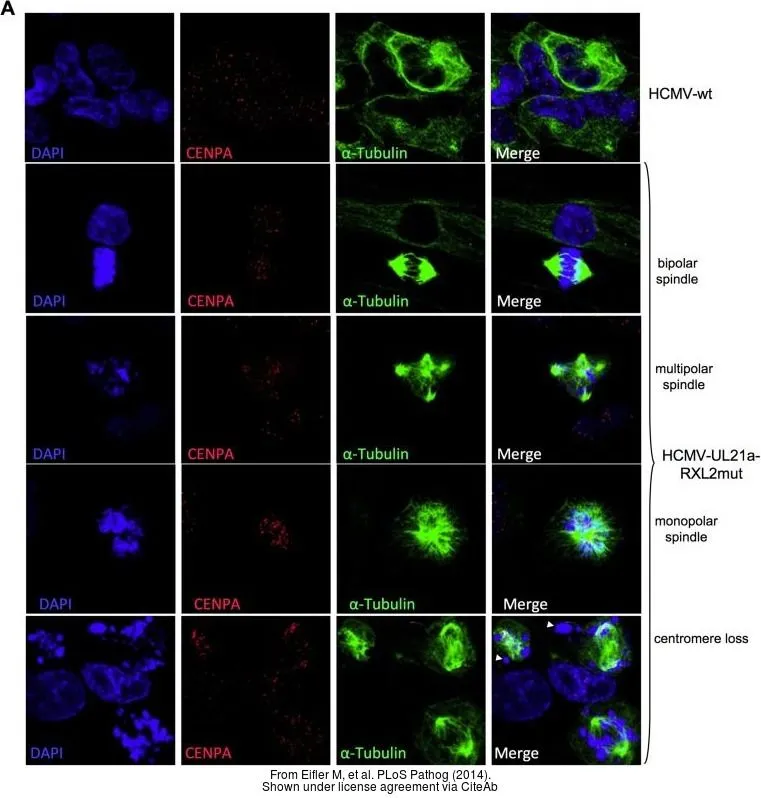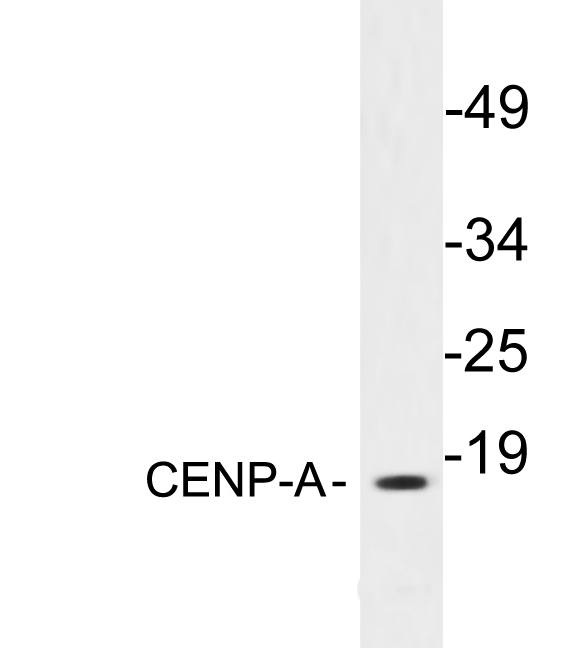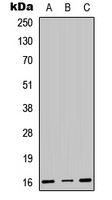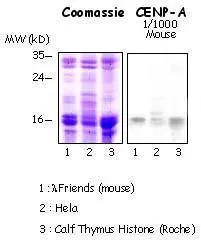
Hela cells (human), Friend cells (mouse) and calf thymus (Roche). 5 g acid-extracted histones were loaded per lane. Images taken following 5 min exposure. 1:1000 dilution. Lane 1: Friend cells (mouse); Lane 2: Hela cells (human); Lane 3: Calf thymus. This
CENPA antibody [3-19]
GTX13939
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Neutralisation/Blocking
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityC. Elegans, Chicken, Human
TargetCENPA
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCENPA antibody [3-19]
- Delivery Days Customer9
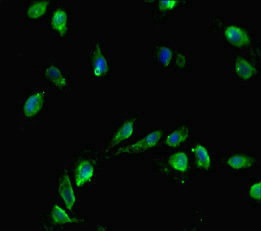
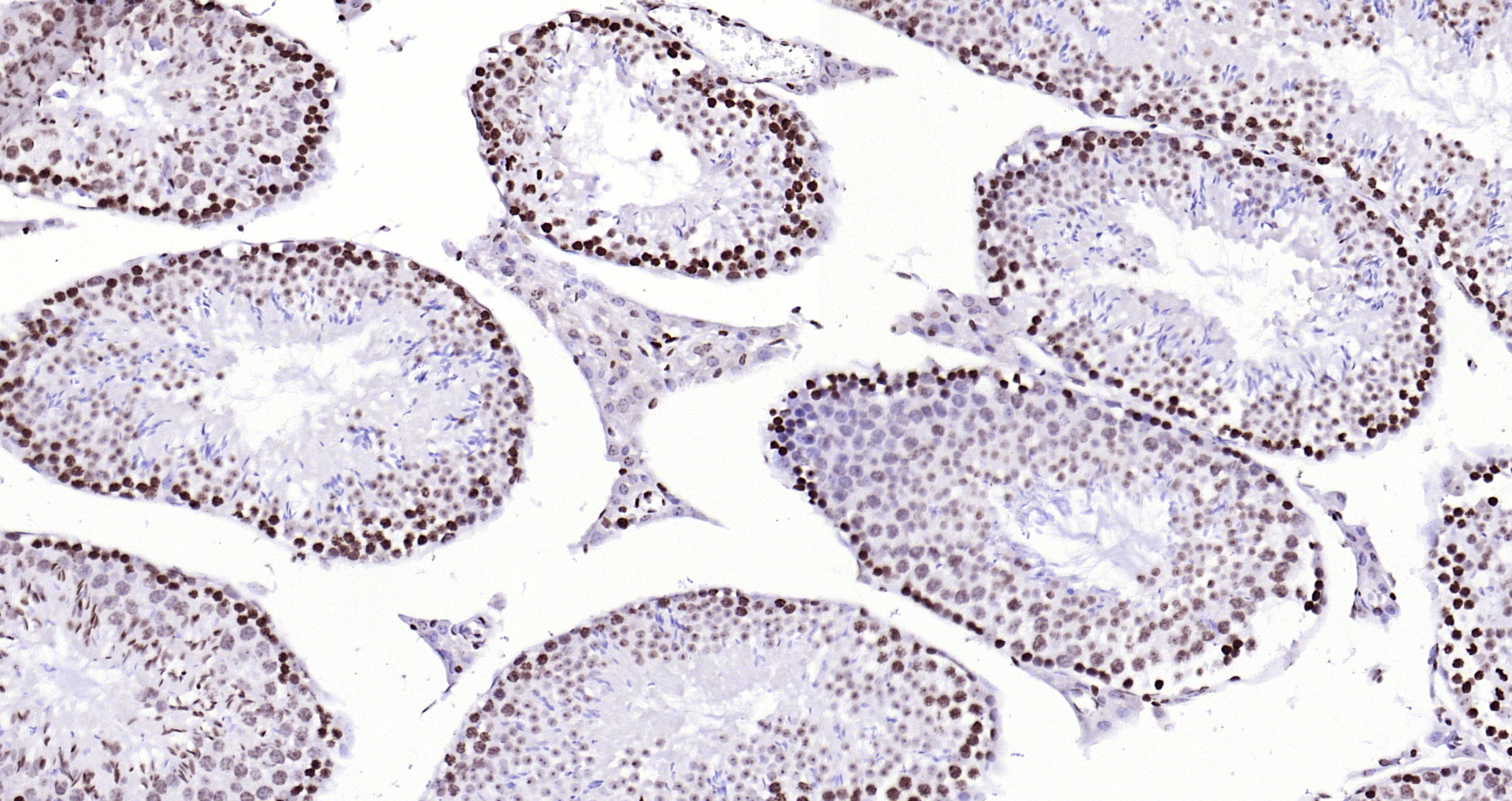
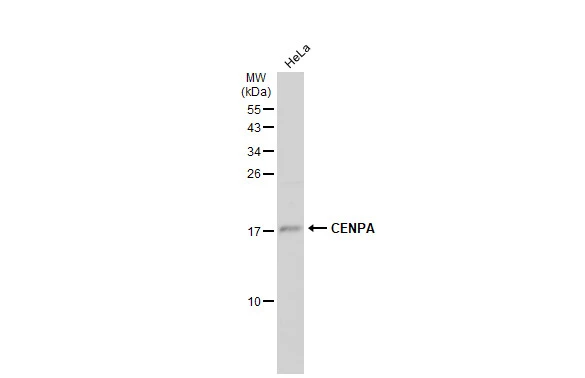
- Application Supplier NoteICC: Use at a concentration of 10 microg/ml. IHC: Use at a concentration of 5 microg/ml. For paraffin embedded sections, heat treatment may be necessary. Microwave sections 2 times for 10 minutes each in citrate buffer (pH 6.5). WB: Use at a concentration of 1 microg/ml. Detects a band of approximately 18 kDa (predicted molecular weight: 16 kDa). Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. User review: This antibody is great for immunofluorescence on human cells (primary fibroblasts and transformed cell lines such as HeLa, HT1080, A549, H1299). Works well with various fixation conditions, including 1-4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), -20C methanol, 2% PFA followed by -20C methanol, and on unfixed preparations. We routinely use it at a dilution of 1:200-1:400.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Neutralisation/Blocking
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID3-19
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1058
- Target nameCENPA
- Target descriptioncentromere protein A
- Target synonymsCENP-A, CenH3, histone H3-like centromeric protein A, centromere autoantigen A, centromere protein A, 17kDa, centromere-specific histone
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP49450
- Protein NameHistone H3-like centromeric protein A
- Scientific DescriptionCentromeres are the differentiated chromosomal domains that specify the mitotic behavior of chromosomes. This gene encodes a centromere protein which contains a histone H3 related histone fold domain that is required for targeting to the centromere. Centromere protein A is proposed to be a component of a modified nucleosome or nucleosome-like structure in which it replaces 1 or both copies of conventional histone H3 in the (H3-H4)2 tetrameric core of the nucleosome particle. The protein is a replication-independent histone that is a member of the histone H3 family. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]
- ReactivityC. Elegans, Chicken, Human
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Sgo1 interacts with CENP-A to guide accurate chromosome segregation in mitosis.Read this paper
- PP6 regulation of Aurora A-TPX2 limits NDC80 phosphorylation and mitotic spindle size.Read this paper