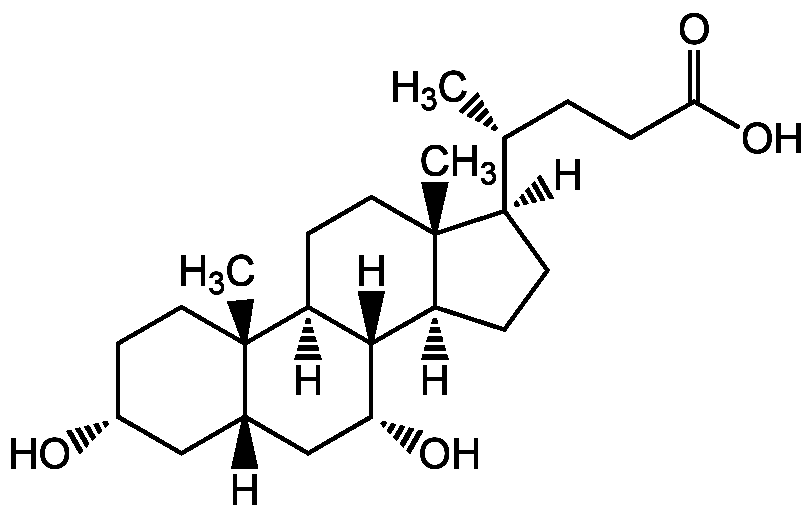
Chemical Structure
Chenodeoxycholic acid [474-25-9] [474-25-9]
AG-CN2-0410
CAS Number474-25-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight392.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameChenodeoxycholic acid [474-25-9] [474-25-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number474-25-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC24H40O4
- Molecular Weight392.6
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 474-25-9. Formula: C24H40O4. MW: 392.6. Synthetic. Originally isolated from bile. Cytotoxic hydrophobic primary bile acid. Activator of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that is hepatoprotective and regulates bile acid synthesis (cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) suppression), conjugation and transport, as well as genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism and. Bile acid-controlled signaling pathways are promising novel targets to treat such metabolic diseases as obesity, type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Inhibitor of 5beta-reductase (AKR1D1). Potent selective inhibitor of DD2 (AKR1C2). Potent inhibitor of 11beta-HSD1 dehydrogenase. Changes tumor cell viability via IL-6 pathway. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory compound. Modulates oxidative stress. Differentiation regulator of mouse embryonic stem cells. Used for dissolution of cholesterol gallstones. - Cytotoxic hydrophobic primary bile acid [1]. Activator of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that is hepatoprotective and regulates bile acid synthesis (cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) suppression), conjugation and transport, as well as genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism and [4-6, 14]. Bile acid-controlled signaling pathways are promising novel targets to treat such metabolic diseases as obesity, type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis [1, 8, 9, 12]. Inhibitor of 5beta-reductase (AKR1D1) [10, 15]. Potent selective inhibitor of DD2 (AKR1C2) [3]. Potent inhibitor of 11beta-HSD1 dehydrogenase [7]. Changes tumor cell viability via IL-6 pathway [11]. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer [13]. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory compound. Modulates oxidative stress [2, 16]. Differentiation regulator of mouse embryonic stem cells [17]. Used for dissolution of cholesterol gallstones.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


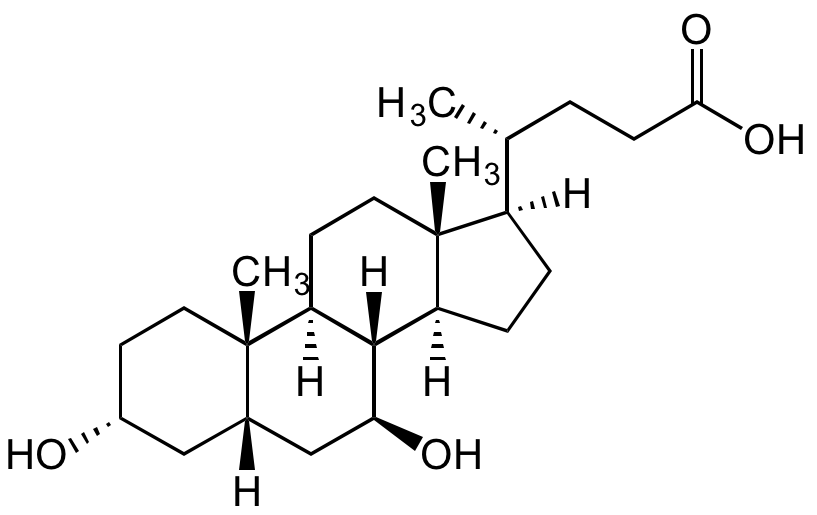
![Chenodeoxycholic acid [474-25-9] [474-25-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/4E/CgoaEGayG4SEXnpoAAAAADROilw269.png)