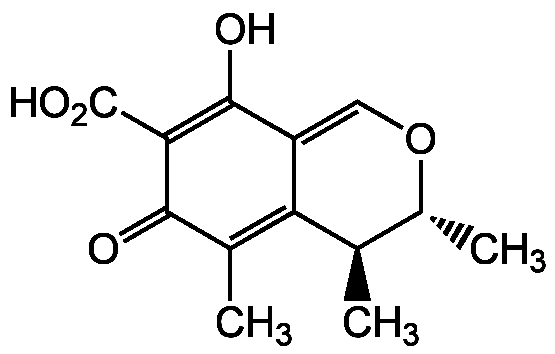
Chemical Structure
Citrinin [518-75-2] [518-75-2]
AG-CN2-0101
CAS Number518-75-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight250.3
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCitrinin [518-75-2] [518-75-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number518-75-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC13H14O5
- Molecular Weight250.3
- Scientific DescriptionAntibiotic [1, 2]. Antiprotozoal. Antimicrobial [3, 6]. Cytotoxic and genotoxic in various mammalian cells [4]. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) activator [5-7]. Apoptosis inducer [7-9, 14]. ERK and JNK signaling pathways activator [10]. Nephrotoxic mycotoxin [11]. Suppresses NO and iNOS expression via inhibition of the JAK/STAT-1alpha and NF-kappaB signaling pathways [12]. Tubulin polymerization and mitotic spindle assembly inhibitor [13]. Increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) [14]. Induces cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 and G2/M phase [13,14]. - Chemical. CAS: 518-75-2. Formula: C13H14O5. MW: 250.3. Isolated from Penicillium citrinum strain FKI-4836. Antibiotic. Antiprotozoal. Antimicrobial. Cytotoxic and genotoxic in various mammalian cells. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) activator. Apoptosis inducer. ERK and JNK signaling pathways activator. Nephrotoxic mycotoxin. Suppresses NO and iNOS expression via inhibition of the JAK/STAT-1alpha and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Tubulin polymerization and mitotic spindle assembly inhibitor. Increases reactive oxygen species (ROS). Induces cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 and G2/M phase.
- SMILESC[C@H]1OC=C2C(O)=C(C(O)=O)C(=O)C(C)=C2[C@@H]1C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UN NumberUN 3462
- UNSPSC12352200

![Citrinin [518-75-2] [518-75-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/DC/CgoaEWayRNmEADNTAAAAAOV6rlI099.png)