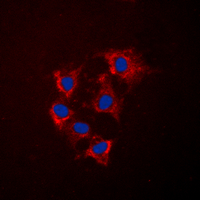
ICC/IF analysis of formalin-fixed HeLa cells using GTX56030 COL4A5 antibody. Red : Primary antibody Blue : DAPI Permeabilization : 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes
COL4A5 antibody
GTX56030
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetCOL4A5
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCOL4A5 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:1000. ICC/IF: 1:100 - 1:500. IHC-P: 1:100 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1287
- Target nameCOL4A5
- Target descriptioncollagen type IV alpha 5 chain
- Target synonymsASLN, ATS, ATS1, CA54, collagen alpha-5(IV) chain, collagen IV, alpha-5 polypeptide, collagen of basement membrane, alpha-5 chain, collagen, type IV, alpha 5, dA149D17.3, dA24A23.1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP29400
- Protein NameCollagen alpha-5(IV) chain
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes one of the six subunits of type IV collagen, the major structural component of basement membranes. Mutations in this gene are associated with X-linked Alport syndrome, also known as hereditary nephritis. Like the other members of the type IV collagen gene family, this gene is organized in a head-to-head conformation with another type IV collagen gene so that each gene pair shares a common promoter. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Troponin T amino acid mutation (deltaK210) knock-in mice as a neonatal dilated cardiomyopathy model. Tanihata J et al., 2021 Mar, Pediatr ResRead this paper