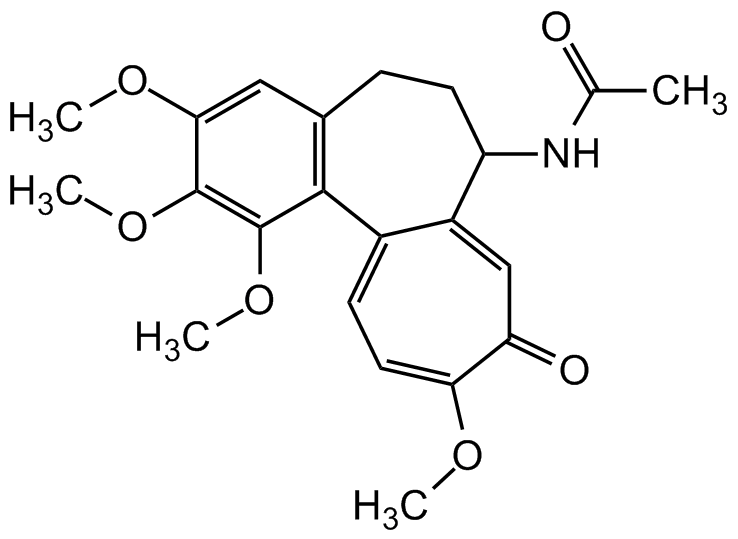
Chemical Structure
Colchicine
AG-CN2-0048
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameColchicine
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number64-86-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC22H25NO6
- Molecular Weight399.4
- Scientific DescriptionAnti-cancer compound [5]. Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Depolymerizes microtubules and limits microtubule formation (inactivates spindle fibre formation) [1, 2, 5, 6]. Inhibits mitosis during cell division at metaphase by inhibiting spindle formation [6]. Anti-inflammatory compound [7, 9]. Suppresses monosodium urate crystal-induced NLRP3/NALP3 inflammasome-driven caspase-1 activation, IL-1beta processing and release, and L-selectin expression on neutrophils at micromolar concentrations. Blocks the release of a crystal-derived chemotactic factor from neutrophil lysosomes, blocks neutrophil adhesion to, and inhibits monosodium urate crystal-induced production of superoxide anions from neutrophils at nanomolar concentrations [7]. Drug used in treatment of gout, familial Mediterranean fever, pericarditis and Behects disease. Investigated for its anti-cancer activity [5, 8, 9]. It has a narrow therapeutic index with no clear-cut distinction between nontoxic, toxic and lethal doses, causing substantial confusion among clinicians [8]. Apoptosis inducer in a variety of normal and tumor cell lines [3, 4]. Inhibitor of autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Inhibits acetylated a-tubulin mediated dynein dependent transport of mitochondria and subsequent apposition of ASC on mitochondria to NLRP3 on the endoplasmic reticulum in vitro and in vivo. - Chemical. CAS: 64-86-8. Formula: C22H25NO6. MW: 399.4. Isolated from Colchicum autumnale. Anti-cancer compound. Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Depolymerizes microtubules and limits microtubule formation (inactivates spindle fibre formation). Inhibits mitosis during cell division at metaphase by inhibiting spindle formation. Anti-inflammatory compound. Suppresses monosodium urate crystal-induced NLRP3/NALP3 inflammasome-driven caspase-1 activation, IL-1beta processing and release, and L-selectin expression on neutrophils at micromolar concentrations. Blocks the release of a crystal-derived chemotactic factor from neutrophil lysosomes, blocks neutrophil adhesion to, and inhibits monosodium urate crystal-induced production of superoxide anions from neutrophils at nanomolar concentrations. Drug used in treatment of gout, familial Mediterranean fever, pericarditis and Behects disease. Investigated for its anti-cancer activity. It has a narrow therapeutic index with no clear-cut distinction between nontoxic, toxic and lethal doses, causing substantial confusion among clinicians. Apoptosis inducer in a variety of normal and tumor cell lines. Inhibitor of autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Inhibits acetylated a-tubulin mediated dynein dependent transport of mitochondria and subsequent apposition of ASC on mitochondria to NLRP3 on the endoplasmic reticulum in vitro and in vivo.
- SMILESCOC1=CC2=C(C(OC)=C1OC)C1=CC=C(OC)C(=O)C=C1C(CC2)NC(C)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UN NumberUN 3462
- UNSPSC12352200

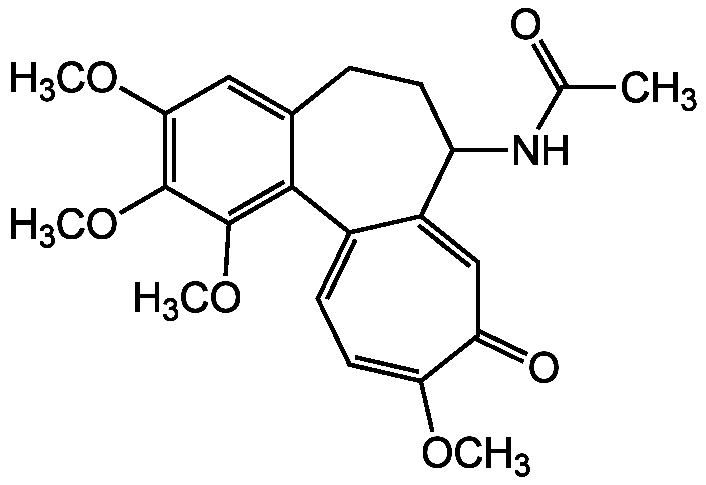

![Colchicine [64-86-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/34/6F/CgoaEGarc52ETJAkAAAAAPI4q7Y437.png)