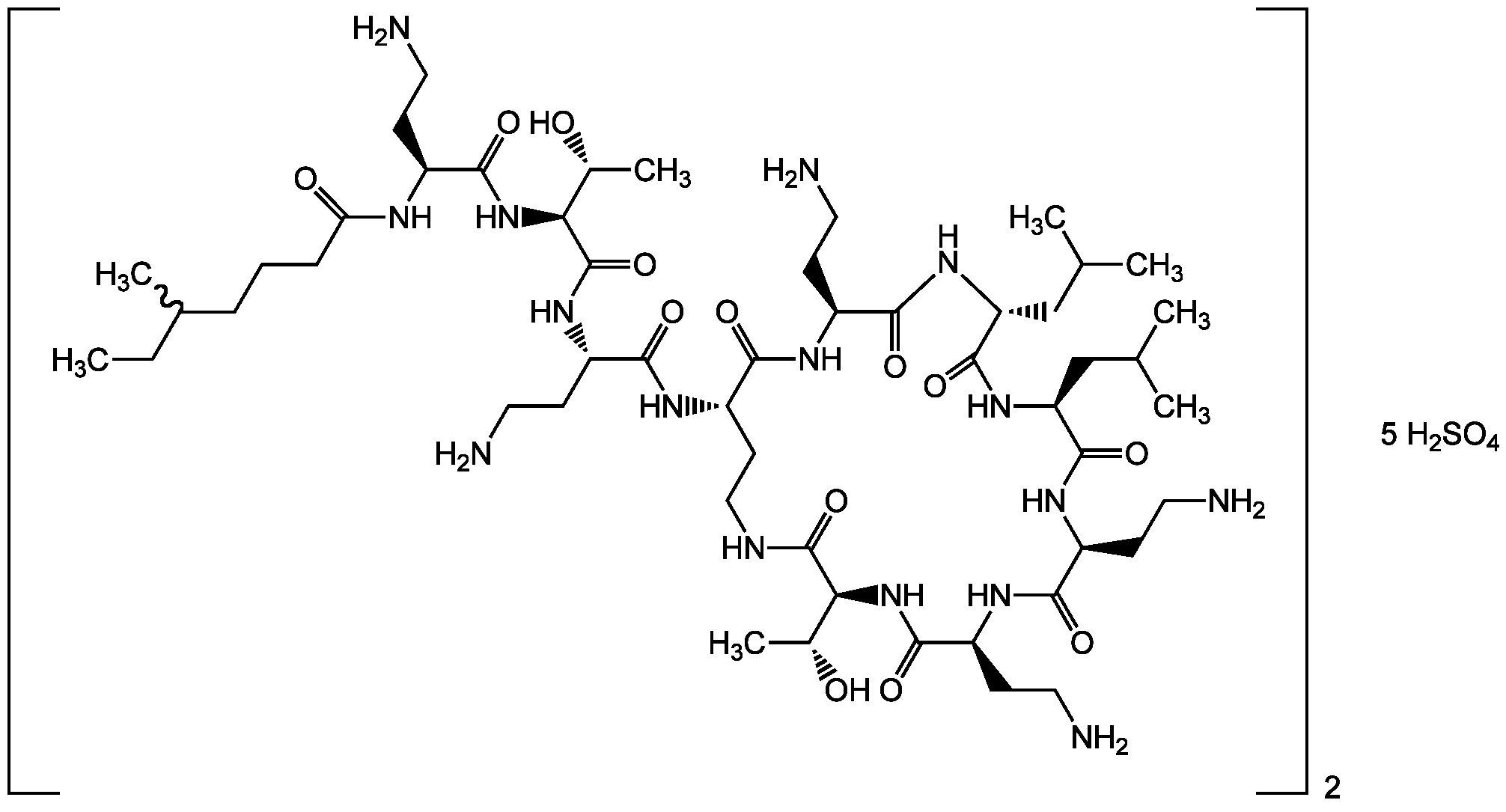
Chemical Structure
Colistin sulfate (USP Grade) [1264-72-8] [1264-72-8]
AG-CN2-0065
CAS Number1264-72-8
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight2801.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameColistin sulfate (USP Grade) [1264-72-8] [1264-72-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number1264-72-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular Formula2(C52H98N16O13) . 5(H2SO4) (unspec.)
- Molecular Weight2801.7
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 1264-72-8. Formula: 2(C52H98N16O13) . 5(H2SO4) (unspec.). MW: 2801.7. Isolated from Bacillus polymyxa. Very potent polymyxin antibiotic. Has only one amino acid difference compared to polymyxin B. Antimicrobial. Targets the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Competitively displaces divalent cations (Ca2+ and Mg2+) from the negatively-charged phosphate groups LPS, causing disruption of the membrane. This increases the permeability of the cell envelope, leakage of cell contents, leading to apoptosis and cell death. Used against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. - Very potent polymyxin antibiotic. Has only one amino acid difference compared to polymyxin B. Antimicrobial. Targets the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Competitively displaces divalent cations (Ca2+ and Mg2+) from the negatively-charged phosphate groups LPS, causing disruption of the membrane. This increases the permeability of the cell envelope, leakage of cell contents, leading to apoptosis and cell death. Used against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections.
- SMILESCCC(C)CCCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCN)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCN)C(=O)N[C@H]1CCNC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H](CCN)NC(=O)[C@H](CCN)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCN)NC1=O)[C@@H](C)O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UN NumberUN 3462
- UNSPSC12352200

![Colistin sulfate [1264-72-8] [1264-72-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/93/CgoaEGY7N36EAM9RAAAAAKg62fE761.png)