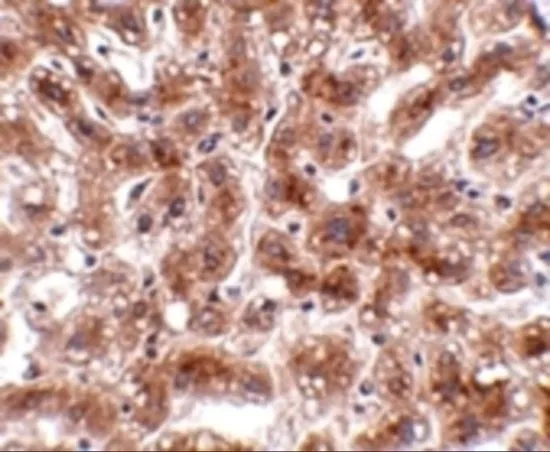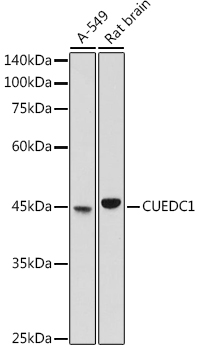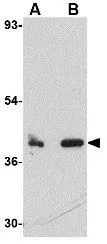
WB analysis of rat liver tissue lysate using GTX85378 CUEDC1 antibody. Working concentration : (A) 0.5 and (B) 1 μg/ml
CUEDC1 antibody
GTX85378
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCUEDC1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCUEDC1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.5 - 1 microg/mL. IHC-P: 2 microg/mL. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID404093
- Target nameCUEDC1
- Target descriptionCUE domain containing 1
- Target synonymsCUE domain-containing protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9NWM3
- Protein NameCUE domain-containing protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThe CUE (coupling of ubiquitin conjugation to endoplasmic reticulum degradation) domain is an evolutionarily conserved, ~40 amino acid monoubiquitin-binding domain that mediates intramolecular monoubiquitylation. CUE domains are present in eukaryotic proteins that are involved in ubiquitination and protein trafficking pathways and may be required for ubiquitination of the proteins in which they are found. CUEDC1 (CUE domain-containing protein 1) is a 386 amino acid protein that contains one CUE domain, suggesting a possible role in protein trafficking and degradation pathways. Two isoforms of CUEDC1 exist due to alternative splicing events. Defects in the gene encoding CUEDC1 may be associated with early stage cervical cancer, implicating CUEDC1 as a potential tumor marker. CUEDC1 antibody will not cross-react with CUEDC2.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Cui Y, Song Y, Yan S, et al. CUEDC1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the TβRI/Smad signaling pathway and suppresses tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 2020,12(20):20047-20068. doi: 10.18632/aging.103329Read this paper