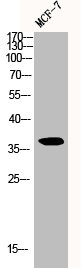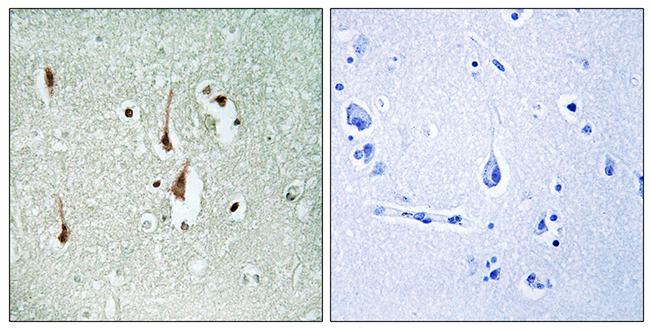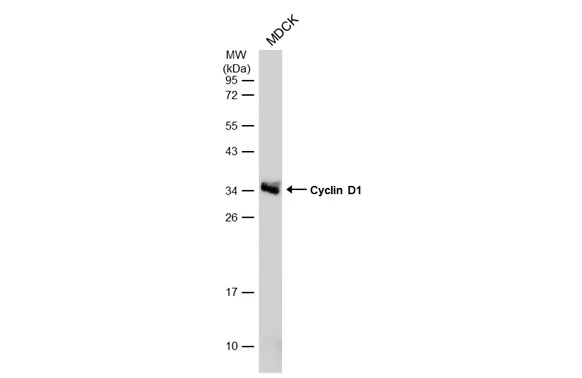
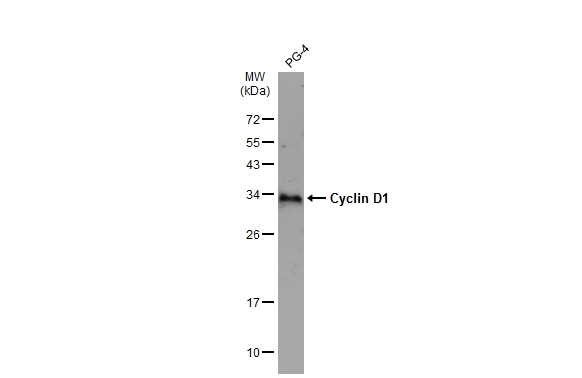
Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody (GTX108624) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.
Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3]
GTX108624
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityCanine, Feline, Human, Rat
TargetCCND1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCyclin D1 antibody [N1C3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. ELISA: 1:1000-1:10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID595
- Target nameCCND1
- Target descriptioncyclin D1
- Target synonymsBCL1, D11S287E, PRAD1, U21B31, G1/S-specific cyclin-D1, B-cell CLL/lymphoma 1, B-cell lymphoma 1 protein, BCL-1 oncogene, PRAD1 oncogene
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP24385
- Protein NameG1/S-specific cyclin-D1
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance throughout the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK4 or CDK6, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. This protein has been shown to interact with tumor suppressor protein Rb and the expression of this gene is regulated positively by Rb. Mutations, amplification and overexpression of this gene, which alters cell cycle progression, are observed frequently in a variety of tumors and may contribute to tumorigenesis. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityCanine, Feline, Human, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] detects Cyclin D1 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: SK-N-SH cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Cyclin D1 protein stained by Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:500. Scale bar = 10 μm. Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] detects Cyclin D1 protein at cytoplasm and nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: SK-N-SH cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Cyclin D1 protein stained by Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:500. Scale bar = 10 μm.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108624/GTX108624_42550_20161109_IFA_w_23060120_147.webp)
![Wild-type (WT) and Cyclin D1 knockout (KO) HeLa cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Wild-type (WT) and Cyclin D1 knockout (KO) HeLa cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108624/GTX108624_43754_20191108_WB_KO_watermark_w_23060120_218.webp)
![Immunoprecipitation of Cyclin D1 protein from MCF-7 whole cell extracts using 5 μg of Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624). Western blot analysis was performed using Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624). EasyBlot anti-Rabbit IgG (GTX221666-01) was used as a secondary reagent. Immunoprecipitation of Cyclin D1 protein from MCF-7 whole cell extracts using 5 μg of Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624). Western blot analysis was performed using Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624). EasyBlot anti-Rabbit IgG (GTX221666-01) was used as a secondary reagent.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108624/GTX108624_40401_20151204_IP_w_23060120_745.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108624/GTX108624_42578_20200403_WB_competitor_watermark_w_23060120_493.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108624/GTX108624_43971_20200612_WB_23072519_431.webp)
![Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cyclin D1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX108624) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108624/GTX108624_45329_20240216_WB_24021917_984.webp)