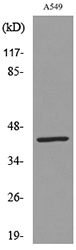
![WB analysis of MCF-7 cell lysate using GTX27754 Cytokeratin 19 antibody [A53-B/A2]. Lane 1,2 : GTX27755 Lane 3,4 : GTX27754 WB analysis of MCF-7 cell lysate using GTX27754 Cytokeratin 19 antibody [A53-B/A2]. Lane 1,2 : GTX27755 Lane 3,4 : GTX27754](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX27754/GTX27754_20191028_WB_1_w_23060722_247.webp)
WB analysis of MCF-7 cell lysate using GTX27754 Cytokeratin 19 antibody [A53-B/A2]. Lane 1,2 : GTX27755 Lane 3,4 : GTX27754
Cytokeratin 19 antibody [A53-B/A2]
GTX27754
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetKRT19
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCytokeratin 19 antibody [A53-B/A2]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDA53-B/A2
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3880
- Target nameKRT19
- Target descriptionkeratin 19
- Target synonymsCK19, K19, K1CS, keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19, 40-kDa keratin intermediate filament, CK-19, cytokeratin 19, keratin 19, type I, keratin, type I, 40-kd
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP08727
- Protein NameKeratin, type I cytoskeletal 19
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin family. The keratins are intermediate filament proteins responsible for the structural integrity of epithelial cells and are subdivided into cytokeratins and hair keratins. The type I cytokeratins consist of acidic proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains. Unlike its related family members, this smallest known acidic cytokeratin is not paired with a basic cytokeratin in epithelial cells. It is specifically expressed in the periderm, the transiently superficial layer that envelopes the developing epidermis. The type I cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 17q12-q21. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
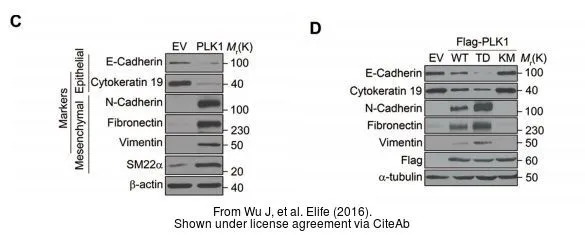
- Polo-like kinase 1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes epithelial cell motility by activating CRAF/ERK signaling. Wu J et al., 2016 Mar 22, ElifeRead this paper






![WB analysis of MCF-7 cell lysate using GTX27755 Cytokeratin 19 antibody [BA-17].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX27755/GTX27755_20191028_WB_1_w_23060722_386.webp)