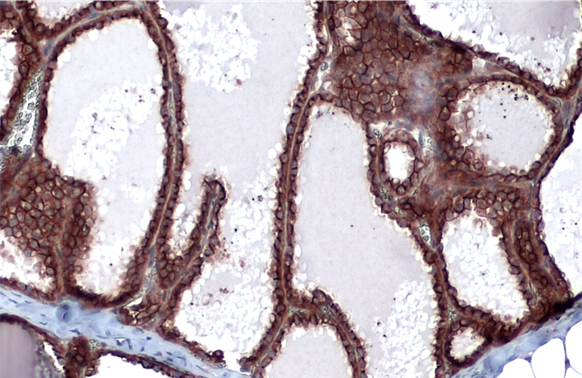
Cytokeratin 19 antibody detects Cytokeratin 19 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded dog mammary gland. Cytokeratin 19 stained by Cytokeratin 19 antibody (GTX112826) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1]
GTX112826
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityCanine, Human, Mouse
TargetKRT19
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3880
- Target nameKRT19
- Target descriptionkeratin 19
- Target synonymsCK19, K19, K1CS, keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19, 40-kDa keratin intermediate filament, CK-19, cytokeratin 19, keratin 19, type I, keratin, type I, 40-kd
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP08727
- Protein NameKeratin, type I cytoskeletal 19
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin family. The keratins are intermediate filament proteins responsible for the structural integrity of epithelial cells and are subdivided into cytokeratins and hair keratins. The type I cytokeratins consist of acidic proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains. Unlike its related family members, this smallest known acidic cytokeratin is not paired with a basic cytokeratin in epithelial cells. It is specifically expressed in the periderm, the transiently superficial layer that envelopes the developing epidermis. The type I cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 17q12-q21. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityCanine, Human, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] detects Cytokeratin 19 protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse tongue. Cytokeratin 19 stained by Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] (GTX112826) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] detects Cytokeratin 19 protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse tongue. Cytokeratin 19 stained by Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] (GTX112826) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112826/GTX112826_44132_20211005_IHC-P_M_w_23060500_204.webp)
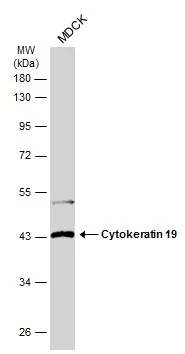
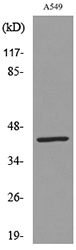
![Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] (GTX112826) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole cell extract (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] (GTX112826) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112826/GTX112826_40079_20201127_WB_w_23060500_778.webp)
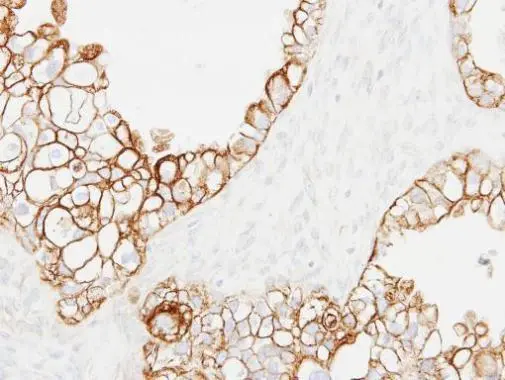
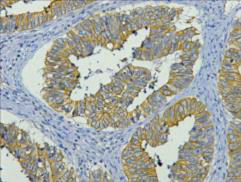
![Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] detects Cytokeratin 19 protein at cytoplasm in human lung adenocarcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human lung adenocarcinoma. Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] (GTX112826) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] detects Cytokeratin 19 protein at cytoplasm in human lung adenocarcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human lung adenocarcinoma. Cytokeratin 19 antibody [N1C1] (GTX112826) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112826/GTX112826_40079_20151227_IHC-P_w_23060500_259.webp)





![WB analysis of MCF-7 cell lysate using GTX27754 Cytokeratin 19 antibody [A53-B/A2]. Lane 1,2 : GTX27755 Lane 3,4 : GTX27754](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX27754/GTX27754_20191028_WB_1_w_23060722_247.webp)