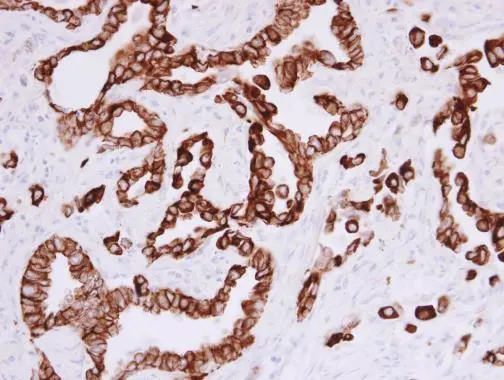
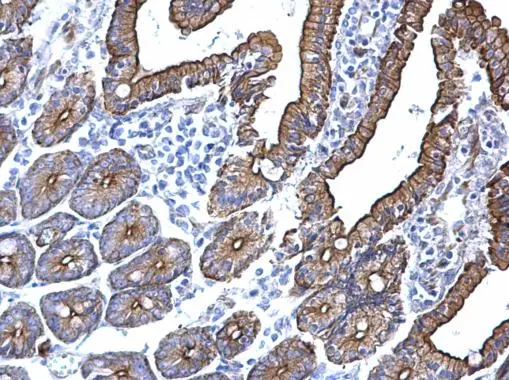
Cytokeratin 5 antibody detects Cytokeratin 5 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm in human breast carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma. Cytokeratin 5 antibody (GTX113219) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min
Cytokeratin 5 antibody
GTX113219
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetKRT5
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCytokeratin 5 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.35 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3852
- Target nameKRT5
- Target descriptionkeratin 5
- Target synonymsCK5, DDD, DDD1, EBS1, EBS2, EBS2A, EBS2B, EBS2C, EBS2D, EBS2E, EBS2F, K5, KRT5A, keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5, 58 kda cytokeratin, CK-5, cytokeratin-5, epidermolysis bullosa simplex 2 Dowling-Meara/Kobner/Weber-Cockayne types, keratin 5 (epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Dowling-Meara/Kobner/Weber-Cockayne types), keratin 5, type II, type-II keratin Kb5
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP13647
- Protein NameKeratin, type II cytoskeletal 5
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. The type II cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. This type II cytokeratin is specifically expressed in the basal layer of the epidermis with family member KRT14. Mutations in these genes have been associated with a complex of diseases termed epidermolysis bullosa simplex. The type II cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q12-q13. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

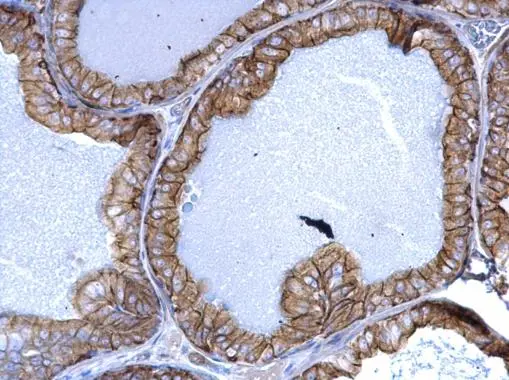




![IHC-P analysis of human esophagus epithelium (A), salivary gland basal cell (B), lung squamous cell carcinoma (C), endometrium admosquamous carcinoma (D) using GTX83080 Cytokeratin 5 antibody [3E2F1].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83080/GTX83080_20170912_IHC-P_w_23061322_411.webp)
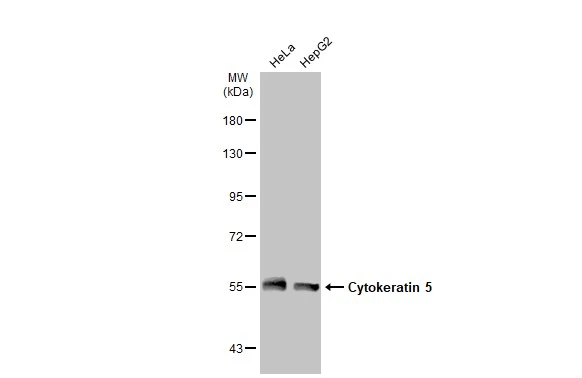
![WB analysis of HeLa cell lysate using GTX83135 Cytokeratin 5 antibody [1E1].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83135/GTX83135_20170912_WB_w_23061322_928.webp)