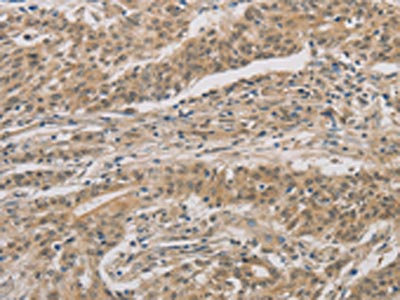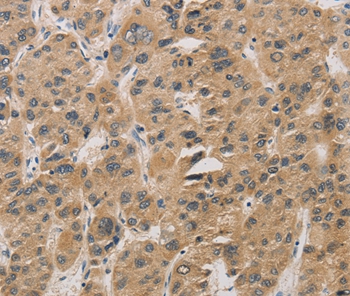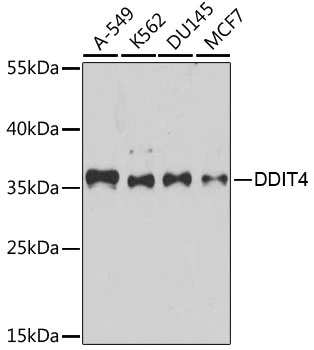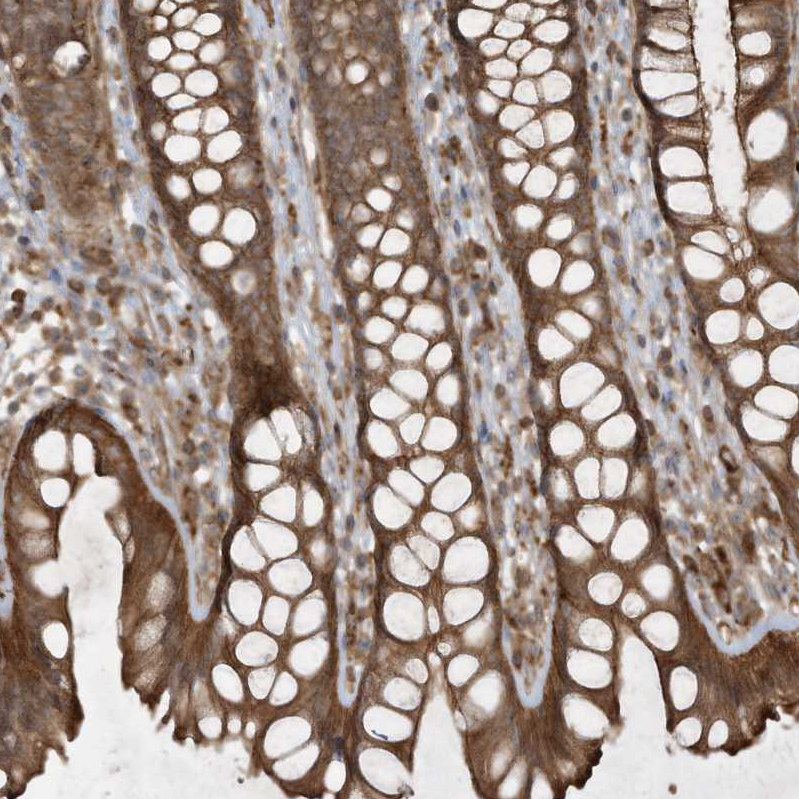
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using CSB-PA151075(DDIT4 Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200)
DDIT4 Antibody
CSB-PA151075
ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetDDIT4
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameDDIT4 Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID54541
- Target nameDDIT4
- Target descriptionDNA damage inducible transcript 4
- Target synonymsDig2, REDD-1, REDD1, DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein, HIF-1 responsive protein RTP801, protein regulated in development and DNA damage response 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9NX09
- Protein NameDNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein
- Scientific DescriptionREDD-1, also designated DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4, dig2 or RTP801, is thought to function in the regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). REDD-1 expression has also been linked to apoptosis, Ab toxicity and the pathogenesis of ischemic diseases. As an HIF-1-responsive gene, REDD-1 exhibits strong hypoxia-dependent upregulation in ischemic cells of neuronal origin. In response to stress due to DNA damage and glucocorticoid treatment, REDD-1 is upregulated at the transcriptional level. REDD-1 negatively regulates the mammalian target of Rapamycin (mTOR), a serine/threonine kinase often referred to as FRAP. It is crucial in the coupling of extra- and intracellular cues to FRAP regulation. The absence of REDD-1 is associated with the development of retinopathy, a major cause of blindness.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161