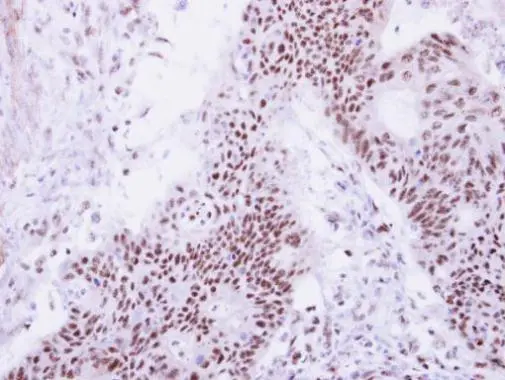
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma, using DDX47(GTX120497) antibody at 1:250 dilution.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min
DDX47 antibody
GTX120497
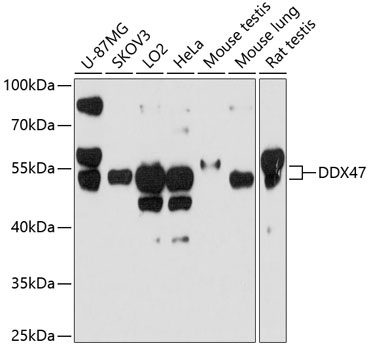
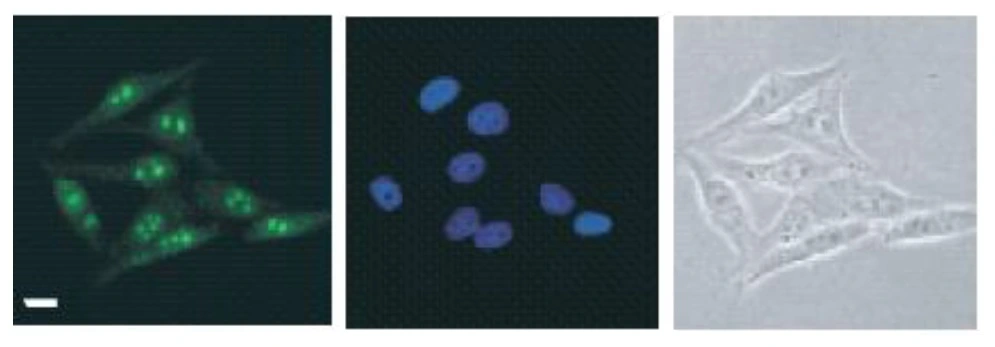
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetDDX47
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameDDX47 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID51202
- Target nameDDX47
- Target descriptionDEAD-box helicase 47
- Target synonymsE4-DBP, HQ0256, MSTP162, RRP3, probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX47, DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 47, DEAD box polypeptide 47, DEAD box protein 47, E4-DEAD box protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9H0S4
- Protein NameProbable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX47
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the DEAD box protein family. DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure, such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. The protein encoded by this gene can shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, and has an RNA-independent ATPase activity. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161